Data Hubs
(2025-08-08T12:58.109Z)
Perplexity Query
(2025-08-08T12:58
.109Z)
Question:
Write a comprehensive one-page article about "Enterprise Data Hubs".
Image References:
Include after the introduction.
Include after the main content section.
Include before the conclusion.
Replace "Enterprise Data Hubs" with the actual vocabulary term in the prompt.
Model:
sonar-pro
Response from sonar-pro:
Enterprise Data Hubs: Unlocking Unified, Agile Data Management in Modern Organizations
 Introduction
Introduction
 Introduction
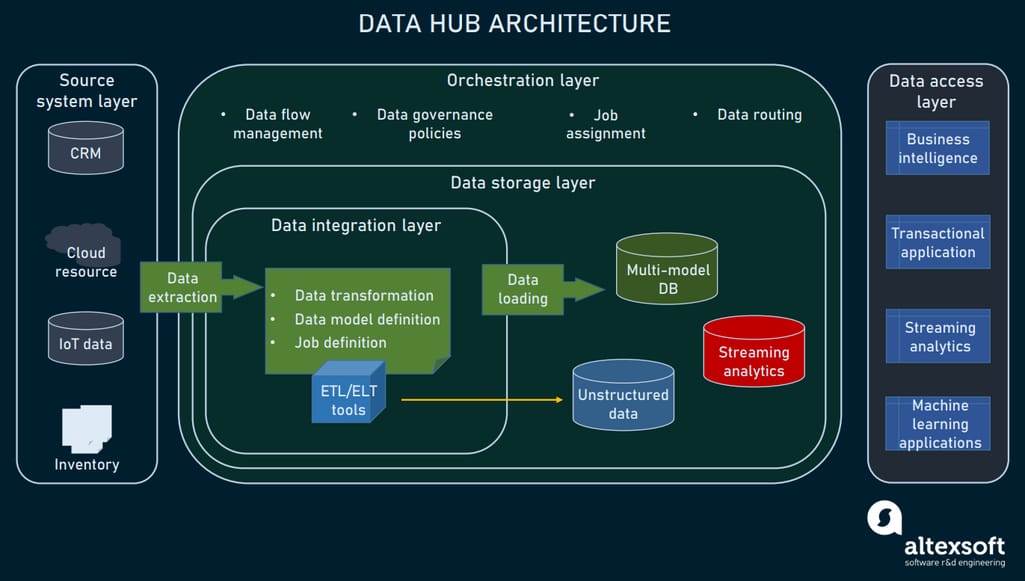
IntroductionAn Enterprise Data Hub (EDH) is a centralized platform designed to aggregate, store, process, and manage vast volumes of data from disparate sources across an organization.
[kvc1e1]
As businesses increasingly rely on data-driven decision-making, having a unified system for handling diverse and rapidly growing data assets is essential for achieving agility, governance, and scale.

Main Content
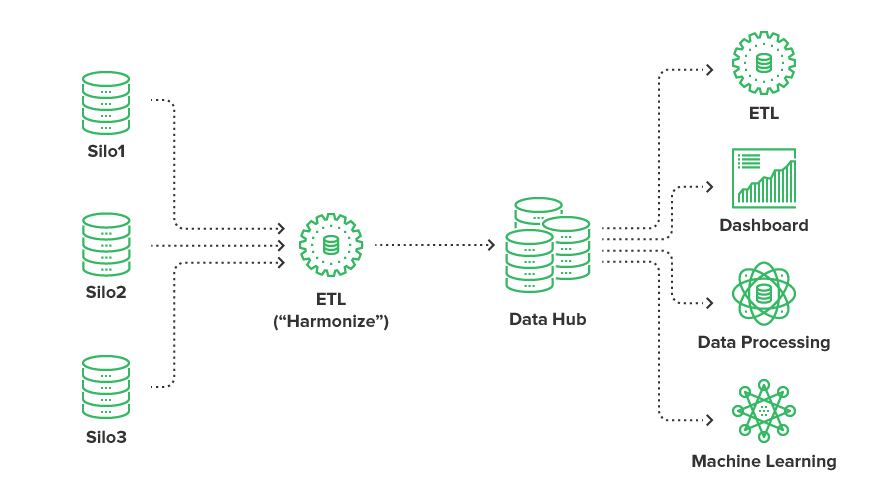
At its core, an enterprise data hub consolidates information from multiple systems—such as CRM, ERP, IoT devices, social media, and more—into a single repository where data is accessible, traceable, and ready for analysis.
[kvc1e1]
Unlike traditional databases or data warehouses, a data hub supports various data types (structured, semi-structured, unstructured) and leverages modern, distributed computing to enable horizontal scalability as data volumes increase.
[kvc1e1]
This architecture allows businesses to plug in new data sources quickly without heavy integration costs or preprocessing, supporting both batch and real-time data processing.
[1wmzk8]
A practical example illustrates this: a multinational retailer might use an enterprise data hub to integrate sales data from stores, supplier inventory feeds, online behavior from its e-commerce platform, and feedback from customer service channels. By centralizing this information, the retailer gains a unified view of operations, enabling better forecasting, personalized marketing, and more responsive supply chain management.
[f729g6]
 The benefits of implementing an enterprise data hub are significant:
The benefits of implementing an enterprise data hub are significant:- Centralized data management and accessibility: Users gain a unified, organization-wide view of data, eliminating silos and making insights easily discoverable. [kvc1e1]
- Scalability and future-proofing: The flexible, distributed architecture accommodates ongoing growth and adoption of future technologies such as AI and advanced analytics. [f729g6]
Despite these advantages, there are challenges to consider. Integrating legacy systems, ensuring consistent data quality across heterogeneous sources, and aligning organizational processes for data governance all require thoughtful planning. Additionally, successfully adopting an EDH often demands investment in skills and change management to encourage company-wide adoption.
[kvc1e1]
[1wmzk8]
Current State and Trends
The adoption of enterprise data hubs is accelerating as organizations seek to break down data silos and enable seamless collaboration between analytics, operations, and business teams. Industries such as finance, healthcare, retail, and manufacturing increasingly implement data hubs to support regulatory reporting, predictive maintenance, and personalized services.
[kvc1e1]
[f729g6]
Key players and technologies in the space include platforms like MarkLogic, Informatica, and Cloudera, which offer robust, scalable EDH solutions with built-in governance and real-time integration features.
[vr2hp0]
Recent developments include advances in agile DataOps, the application of ELT (Extract Load Transform) pipelines for faster data onboarding, and the integration of machine learning modules directly within data hub environments.
[vr2hp0]
As organizations demand more flexible data architectures, data hubs are being enhanced with native support for cloud, hybrid, and multi-cloud deployments. Data Pipelines.
Future Outlook
Looking forward, enterprise data hubs are poised to become even more intelligent and autonomous, leveraging AI-driven automation for Data Quality Management, anomaly detection, and dynamic governance. The rise of industry-wide data sharing, coupled with regulatory pressures for transparency, will reinforce data hubs as the backbone of trusted digital ecosystems. As a result, businesses equipped with advanced EDH capabilities will be best positioned to harness value from emerging data sources and technologies, driving innovation and competitive advantage.
[1wmzk8]
Conclusion
Enterprise data hubs are vital in today’s data-driven world, providing organizations with agile, centralized, and secure frameworks for harnessing data value. As technology and data demands evolve, EDHs will serve as critical enablers of business intelligence, innovation, and growth.
Citations
[kvc1e1] 2025, Jul 18. Enterprise data hub: architecture and use cases. Published: 2024-03-30 | Updated: 2025-07-18
[f729g6] 2025, Apr 24. Top 10 Benefits of implementing a Data Hub with SCIKIQ. Published: 2024-05-17 | Updated: 2025-04-24
[lqc3cw] 2025, Jul 31. What is a Data Hub? - A Complete Guide. Published: 2021-08-20 | Updated: 2025-07-31
[vr2hp0] 2024, Nov 05. Data Hub vs Data Warehouse Comparison. Published: 2023-09-13 | Updated: 2024-11-05
[1wmzk8] 2025, Jan 20. Data Hub Benefits for Effective Data, Analytics and AI .... Published: 2024-04-05 | Updated: 2025-01-20