Multi Modal Databases
No tools found in showcase directive
Debug Info
json
{
"name": "tool-showcase",
"toolPaths": [],
"nodeChildren": [
{
"type": "paragraph",
"children": [
{
"type": "link",
"url": "/toolkit/software-development/databases/surrealdb",
"data": {
"hProperties": {
"data-internal-link": ""
}
},
"children": [
{
"type": "text",
"value": "SurrealDB"
}
]
},
{
"type": "text",
"value": "\n"
},
{
"type": "link",
"url": "/toolkit/software-development/databases/arangodb",
"data": {
"hProperties": {
"data-internal-link": ""
}
},
"children": [
{
"type": "text",
"value": "ArangoDB"
}
]
},
{
"type": "text",
"value": "\n"
},
{
"type": "link",
"url": "/toolkit/software-development/lego-kit-engineering-tools/backend-as-a-service/singlestore",
"data": {
"hProperties": {
"data-internal-link": ""
}
},
"children": [
{
"type": "text",
"value": "SingleStore"
}
]
}
],
"position": {
"start": {
"line": 5,
"column": 1,
"offset": 225
},
"end": {
"line": 7,
"column": 105,
"offset": 453
}
}
}
]
}Deprecation Warning
The ```yaml toolingGallery syntax is deprecated. Please use :::tooling-gallery directive syntax instead.
⚠️ Tool(s) not found:
tag: Multi-Modal-Databases
(2025-07-25T15:32.688Z)
Perplexity Query
(2025-07-25T15:32
.688Z)
Question:
Write a comprehensive one-page article about "Multi-Modal Databases".
Image References:
Include
Introduction
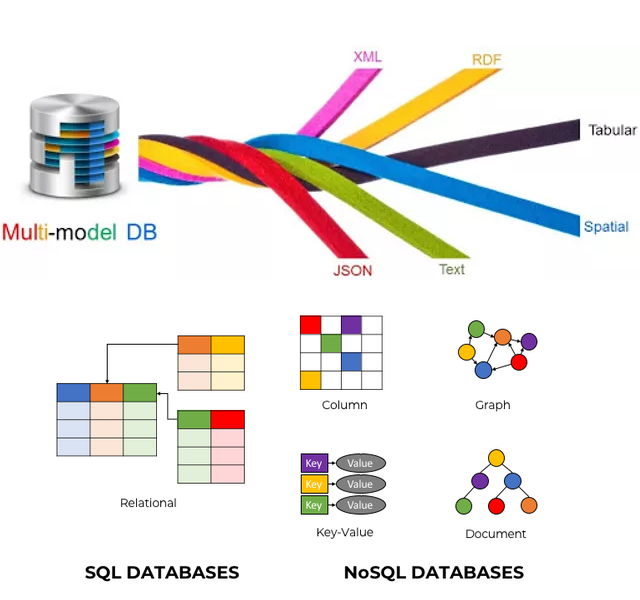
A multi-model database is a database management system capable of storing, querying, and manipulating multiple types of data models—such as relational, document, graph, and key-value—within a single, integrated backend. [^qp1xag] [^b1sq37] [^lwogx0] As organizations increasingly generate and rely on diverse data formats—from structured tables and JSON documents to complex graphs and vector embeddings—traditional single-model databases often fall short. Multi-model databases represent a transformative shift in data management, offering the flexibility to handle varied data needs without the complexity of maintaining multiple, siloed systems. [^qp1xag] [^b1sq37] This convergence of models is not just a technical novelty; it’s a practical necessity in the era of big data, AI, and real-time analytics.
Current State and Trends
The adoption of multi-model databases is accelerating, driven by the demands of modern applications that span structured, semi-structured, and unstructured data. [^qp1xag] [^b1sq37] Leading vendors—such as ArangoDB, SurrealDB, Microsoft Azure Cosmos DB, and MongoDB (with its support for both document and graph models)—are at the forefront, offering robust, scalable platforms for diverse workloads. [^zyh90u] Postgres, originally relational, has also extended its capabilities to support JSON and graph extensions, highlighting the trend toward multi-model functionality even in traditional systems. [^qp1xag]
Recent developments include tighter integration with AI ML Pipelines, as Vector Embeddings become a critical data type for recommendation and search systems. [^qp1xag] There is also growing interest in unified query languages that can traverse multiple models—think of querying product, review, and recommendation data in a single, efficient operation. Open-source contributions and cloud-native deployments are making these technologies more accessible, while industry benchmarks increasingly highlight their cost-efficiency and operational simplicity compared to maintaining multiple, specialized databases. [^qp1xag] [^b1sq37]
Future Outlook
Looking ahead, multi-model databases are poised to become the default choice for enterprises navigating complex, data-rich environments. As AI, IoT, and edge computing proliferate, the ability to natively handle diverse data types within a single system will be a competitive advantage. We can expect further innovation in query optimization, schema governance, and cross-model transactions, along with deeper integration with analytics and AI tooling. The boundary between operational and analytical workloads may blur, as multi-model platforms enable real-time insights across the entire data spectrum.
Conclusion
Multi-model databases represent a paradigm shift in data management, offering unprecedented flexibility and efficiency for organizations contending with diverse and growing data needs. [^qp1xag] [^b1sq37] [^lwogx0] By unifying multiple data models within a single platform, they simplify architecture, reduce complexity, and unlock new possibilities for real-time, cross-model analytics and AI applications. As technology continues to evolve, multi-model databases will play a central role in shaping the future of data-driven innovation.
Sources
[^qp1xag] https://www.navicat.com/en/company/aboutus/blog/3170-how-multi-modal-databases-are-transforming-modern-data-management.html
[^b1sq37] https://www.numberanalytics.com/blog/ultimate-guide-multi-model-databases-big-data
[p6u7m1] Jan 2015. "Multi-model database | En". a multi-model database.. En.
[pzz6dn] Feb 2025. "Multi-Model and Cloud-Native Databases — The Future of Data Management | Medium". Servifyspheresolutions. Medium.