Relational Databases
(2025-09-23T11:38.403Z)
Perplexity Query
(2025-09-23T11:38
.403Z)
Question:
Write a comprehensive one-page article about "Relational Database".
Model: sonar-pro
How Relational Databases Work
A relational database is a type of database that organizes information into tables (or “relations”) made up of rows and columns, allowing for efficient storage, retrieval, and management of structured data.
[i4tbl6]
[ksq77d]
[gp534k]
The significance of relational databases lies in their robust data integrity, flexibility, and scalability, making them foundational for countless business and technology systems worldwide.
[ksq77d]
[gp534k]
In a data-driven age, relational databases provide the reliable structure necessary to support everything from banking transactions to global ecommerce.

Main Content
A relational database stores data in a collection of tables that can be linked through defined relationships, such as primary and foreign keys.
[ksq77d]
[gp534k]
Each table represents an entity (e.g., customers, orders); rows correspond to records, while columns capture attributes. Relationships between tables—like connecting a customer to their orders—are established via shared keys and constraints, ensuring accuracy and consistency.
[i4tbl6]
[ksq77d]
Practical examples and use cases abound. Major banks use relational databases to track customer accounts and transactional histories, ensuring every deposit, withdrawal, and transfer is recorded reliably. Ecommerce platforms use them to relate products, orders, and customers for seamless shopping experiences. Content management systems (CMS) rely on this structure to store, categorize, and control access to articles, images, and user comments.
[ksq77d]
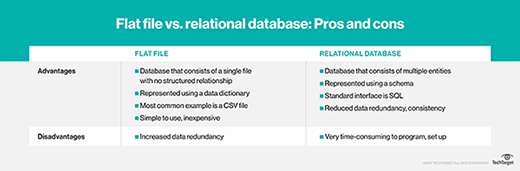
Benefits of relational databases include:
- Community support: Many relational database technologies are open source, yielding active communities and rich tool ecosystems. [i4tbl6]
Challenges and considerations include:
- Complexity: Designing and maintaining a relational database requires careful planning, especially as the system grows in size and complexity.
- Performance: Scaling horizontally can be challenging for very large, high-traffic systems, sometimes prompting migration to NoSQL or hybrid architectures.
- Structure requirements: Relational databases are optimally suited for structured, predictable data; handling unstructured data or rapid schema changes can be limiting. [gp534k]

Current State and Trends
Relational databases maintain strong adoption in industries requiring reliable transaction processing, such as finance, healthcare, retail, and government.
[gp534k]
Key technologies include Oracle Database, Microsoft SQL Server, MySQL, and Postgres, each offering unique advantages for different scenarios.
[gp534k]
The rise of cloud services—like Amazon RDS and Azure SQL Database—is enabling businesses to access relational database power with improved scalability, disaster recovery, and reduced infrastructure management.
[i4tbl6]
[gp534k]
Recent developments feature cloud-native deployments, automated failover, AI-powered management, and the blending of traditional structured data with semi-structured or unstructured formats—often via hybrid approaches combining relational with NoSQL solutions.
[gp534k]
Future Outlook
The future of relational databases will be shaped by integration with cloud and AI technologies, enhanced scalability, and broader support for big data and unstructured information.
[gp534k]
As data volumes and application demands increase, expect relational database systems to evolve, incorporating smarter analytics, automation, and hybrid data storage—the enduring backbone of mission-critical information systems.
Conclusion
Relational databases remain the gold standard for reliable, structured data management, serving as the engine behind modern transactional and analytical systems. As technology advances, their role will only expand, continually adapting to meet the challenges of our data-driven world.
Citations
Citations
[i4tbl6] 2025, Sep 23. What is a Relational Database? - AWS. Published: 2025-09-10 | Updated: 2025-09-23
[ksq77d] 2025, Sep 21. What is Relational Database? Definition, Benefits, and Use Cases. Published: 2025-02-13 | Updated: 2025-09-21
[gp534k] 2025, Sep 23. Exploring RDBMS: Key Features, Benefits, and Applications - OWOX. Published: 2024-08-06 | Updated: 2025-09-23
[4]: 2025, Sep 23. 8 Advantages of a Relational Database - EASA Software. Published: 2025-06-02 | Updated: 2025-09-23
[5]: 2025, Sep 23. Relational Database: Structure, Benefits, and Key Use Cases. Published: 2025-03-18 | Updated: 2025-09-23
[6]: 2025, Sep 23. What Is A Relational Database (RDBMS)? | Google Cloud. Published: 2025-09-22 | Updated: 2025-09-23
[7]: 2025, Sep 23. What Is a Relational Database? (RDBMS)? - Oracle. Published: 2021-06-18 | Updated: 2025-09-23
[8]: 2025, Sep 23. What is a Relational Database Management System? | Microsoft Azure. Published: 2018-01-01 | Updated: 2025-09-23
[9]: 2025, Sep 22. What is a Relational Database? - IBM. Published: 2021-10-20 | Updated: 2025-09-22

