Containers
The market standard service to implement container-based engineering is Docker, though the engineering influencers have started to rave about ContainerD and Podman.
Containers have proliferated so much, tooling like Kubernetes have popped up to help with Container Orchestration.
(2025-09-23T11:51.373Z)
Perplexity Query
(2025-09-23T11:51
.373Z)
Question:
Write a comprehensive one-page article about "Containers and Containerization in Cloud-Native Software Architecture".
Model: sonar-pro
Containers and Containerization in Cloud-Native Software Architecture
Introduction
Containers are lightweight, portable units for packaging software and its dependencies, enabling consistent operation across diverse computing environments.
[v2trbh]
[5fezxs]
In cloud-native software architecture, containerization plays a pivotal role in building scalable, reliable, and highly efficient applications that fully leverage cloud resources.
[96uq5w]
[5fezxs]
As organizations move toward microservices and distributed systems, containerization has become a cornerstone technology in modern digital transformation.
.jpg)
Main Content
Containerization involves encapsulating application code, libraries, and dependencies within isolated environments called containers.
[v2trbh]
[5fezxs]
Unlike traditional virtual machines—which simulate entire operating systems—containers share the host OS kernel, making them much more resource-efficient and faster to launch.
[v2trbh]
This isolation ensures that applications run uniformly whether on a developer’s laptop or in large-scale production cloud environments.
A popular practical example is the use of Docker to containerize a web application: all runtime dependencies are bundled into a single image that can be deployed on any host running a container runtime. Kubernetes, a dominant container orchestration system, enables automated deployment, scaling, and management of thousands of containers running various microservices across cloud platforms.
[96uq5w]
[5fezxs]
For instance, e-commerce platforms, banking applications, and IoT data pipelines now use containerization to achieve rapid feature releases and seamless scalability.
Benefits of containerization in cloud-native architectures include:
- Scalability: Cloud platforms and orchestrators can quickly start or stop containers in response to demand spikes, supporting dynamic scaling for events like Black Friday sales. [96uq5w]
- Isolation and Security: Containers run independently and securely, minimizing risk and allowing rapid problem containment.
- Efficiency: Containers consume fewer resources compared to virtual machines, improving application density and reducing costs. [v2trbh]
Key applications span sectors such as retail (auto-scaling web services), finance (isolated microservices for fraud detection), healthcare (secure patient data management), and telecommunications (network function virtualization).
However, challenges do exist:
- Complexity in orchestration: Managing thousands of containers requires sophisticated tools such as Kubernetes, which introduces operational and security complexities.
- Persistent storage and networking: Ensuring data durability and network performance in ephemeral and distributed container environments demands specialized solutions.
- Security considerations: Although containers offer isolation, misconfigurations or vulnerabilities can lead to breaches if not managed properly. [v2trbh]
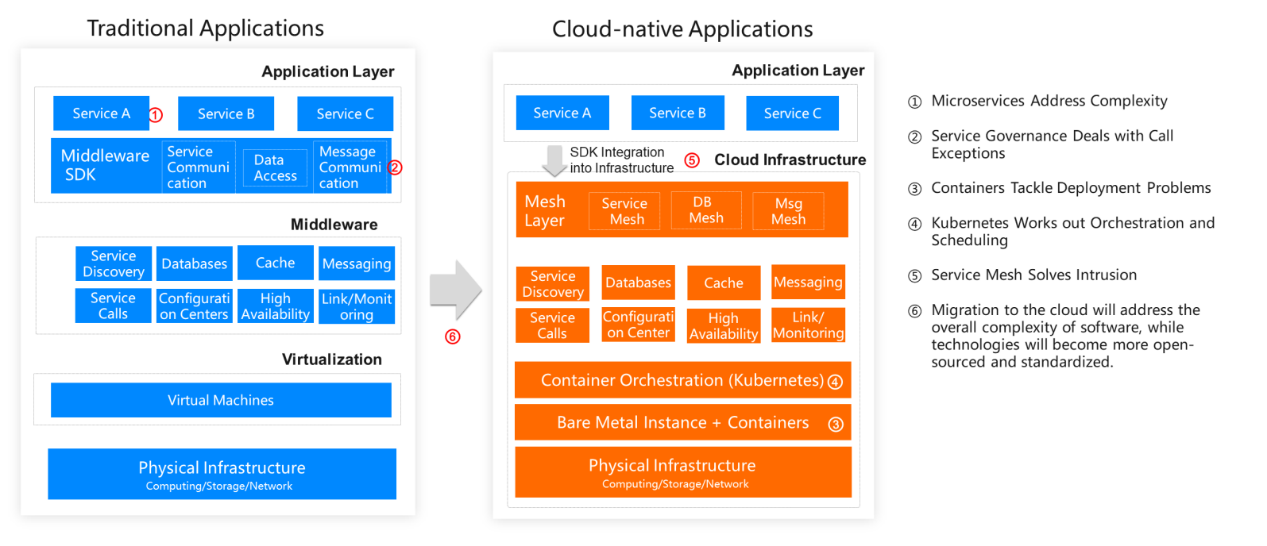
Current State and Trends
The adoption of containers in cloud-native development is now mainstream, driven by platforms such as Docker, Kubernetes, and OpenShift.
[96uq5w]
[5fezxs]
The market continues to grow as enterprises modernize monolithic applications to microservice-based, container-oriented architectures. Kubernetes is widely recognized as the leading orchestration platform, with strong support from public clouds like AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud.
[96uq5w]
[5fezxs]
Key players include Docker Inc., Red Hat (OpenShift), and Google (GKE).
Recent trends include:
- The rise of serverless containers and hybrid cloud deployments.
- Multi-cloud and edge computing, allowing containers to run workloads closer to users for improved performance.
- Advances in container security, such as runtime threat detection, automated vulnerability scanning, and policy enforcement. [v2trbh]
- The proliferation of application registries and continuous integration/continuous deployment (CI/CD) pipelines that leverage containers for agile development cycles. [96uq5w]

Future Outlook
The future of containerization points toward deeper automation, seamless integration with cloud AI/ML workloads, and expanded use in edge computing (for real-time analytics at the network edge). Expect increasing standardization, stronger security frameworks, and advanced orchestration features—making containers even more essential to digital innovation and resilience in cloud-native software architectures.
Conclusion
Containerization has become fundamental to cloud-native architecture for its portability, scalability, and efficiency. As technologies and best practices continue to evolve, containers will shape the future of agile, robust, and innovative application development.
Container Images
Citations
[96uq5w] 2025, Sep 23. What is a Cloud-Native Architecture? - Hazelcast. Published: 2025-01-29 | Updated: 2025-09-23
[v2trbh] 2025, Sep 10. Containerized Architecture: Components and Design Principles. Published: 2021-03-16 | Updated: 2025-09-10
[5fezxs] 2025, Sep 23. What is Cloud Native? - .NET - Microsoft Learn. Published: 2023-12-14 | Updated: 2025-09-23
[5]: 2025, Sep 22. Containers explained: What they are and why you should care. Published: 2023-04-06 | Updated: 2025-09-22
[6]: 2025, Sep 23. What Is Containerization? - Palo Alto Networks. Published: 2020-11-17 | Updated: 2025-09-23


