Telemetry Data
(2025-09-05T13:30.936Z)
Perplexity Query
(2025-09-05T13:30
.936Z)
Question:
Write a comprehensive one-page article about "Telemetry Data".
Model: sonar-pro
Telemetry Data: Real-Time Insights for a Connected World
Telemetry data refers to the automated collection and transmission of measurements from remote or inaccessible systems to a central system for analysis.
[25k5tr]
[j2l5hd]
This technology plays a critical role in modern industries by enabling real-time monitoring, early problem detection, and data-driven decision-making. As digital transformation accelerates, telemetry data matters more than ever, powering everything from connected vehicles to cloud applications and medical devices.
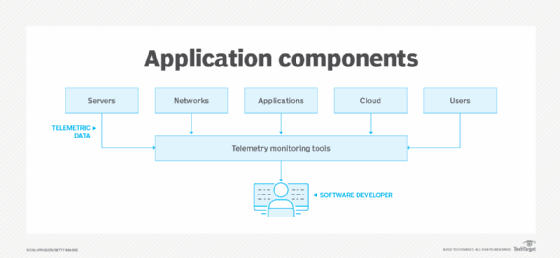
Understanding Telemetry Data
At its core, telemetry data encompasses a suite of technologies that measure and send information automatically from sensors or devices—often located far from human operators—back to a control station.
[25k5tr]
[j2l5hd]
Traditional uses include monitoring spacecraft, satellites, and industrial machinery, but telemetry has expanded dramatically with advancements in wireless communication, cloud computing, and the Internet of Things (IoT).
[j2l5hd]
Practical examples:
- In aviation, plane components send continuous health reports during flight to ground-based maintenance teams.
- Software engineers rely on telemetry from applications to spot bugs and monitor performance across millions of users. [ltw1qe]
- In healthcare, patient vital signs are sent in real-time from wearable monitors to hospitals for remote care. [fr1ww8]
- Utilities use telemetry sensors on pipelines and substations for immediate alerts on leaks or outages.
Key benefits and applications:
- Improved operational efficiency: Constant data flow means teams can monitor systems without manual checks, reducing labor and response time. [25k5tr]
- Performance optimization: Data informs enhancements, helping developers refine software or engineers adjust processes for peak efficiency. [ltw1qe]
- Informed, data-driven decisions: Business leaders, product managers, and IT professionals can steer strategy with hard data, optimizing customer experiences and resource allocations. [21nh1e]
- Safety and compliance: Automated monitoring in safety-critical sectors (like aerospace or medicine) mitigates risks and ensures regulatory compliance. [fr1ww8]
However, collecting and managing telemetry data presents challenges:
- Data overload: The volume of data can overwhelm existing storage and analysis systems, prompting the need for unified platforms. [21nh1e]
- Security and privacy: Sensitive data is vulnerable during transmission, and compliance with regulations (e.g., healthcare or industrial standards) is mandatory.
- Interoperability: Mismatched tools or proprietary data standards may hinder integration, emphasizing the importance of open standards like OpenTelemetry. [21nh1e]
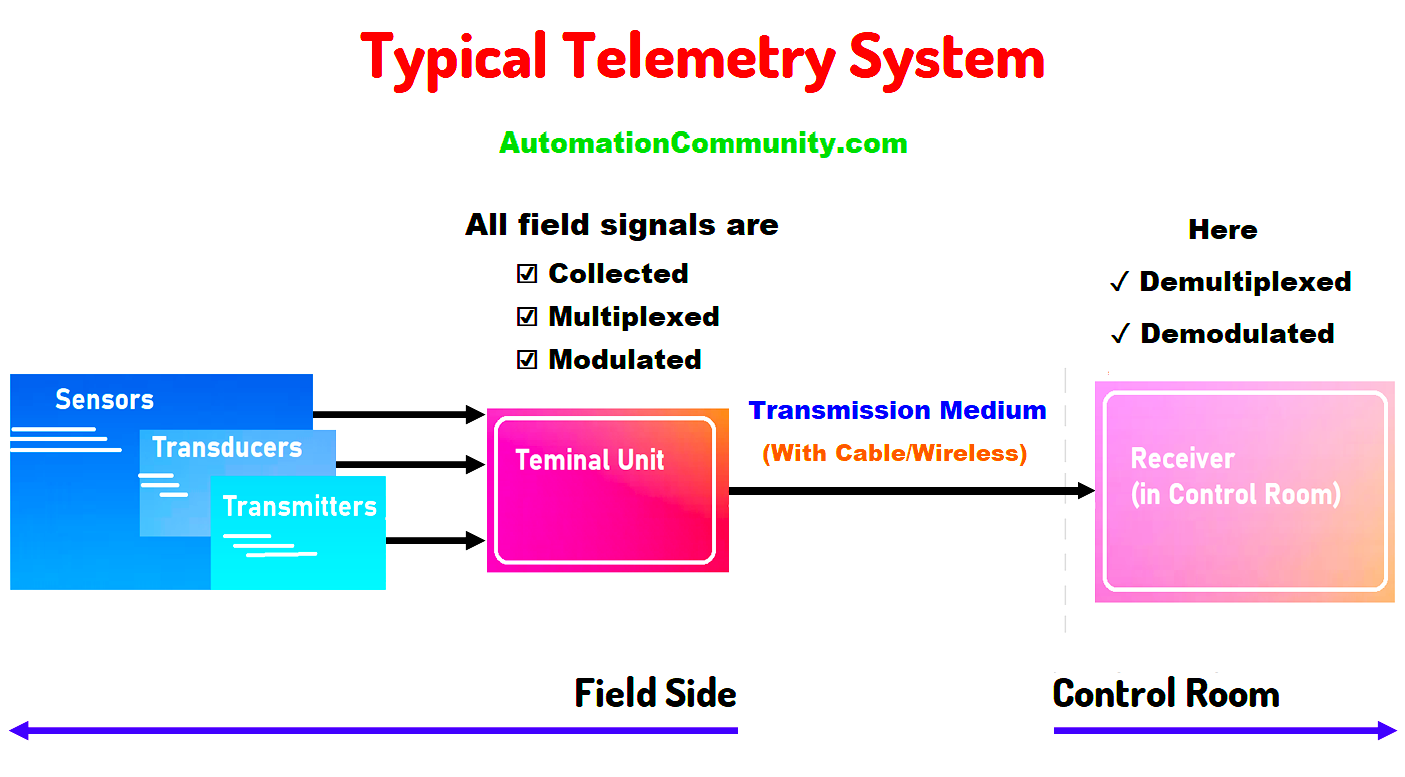
Current State and Trends
Telemetry data is now vital across sectors, including IT and cloud services, automotive, healthcare, logistics, and energy.
[fr1ww8]
Its adoption is rising rapidly, with the global market estimated at over $120 billion in 2023 and projected to surpass $200 billion by 2030 at an annual growth rate exceeding 8%.
[fr1ww8]
Key players in the telemetry ecosystem include hardware vendors (for sensors and IoT devices), software and cloud providers (AWS, Microsoft Azure, Google Cloud), and open-source standards like OpenTelemetry for seamless data integration.
[21nh1e]
In software development, observability platforms such as New Relic and Elastic are shaping how organizations collect, analyze, and act on telemetry insights.
[j2l5hd]
[21nh1e]
Recent innovations focus on unifying telemetry data from diverse sources, improving real-time analytics, and leveraging machine learning for predictive insights and automation.
[21nh1e]
[fr1ww8]
Open standards are becoming increasingly important to ensure compatibility, scalability, and efficient management of large data volumes.

Future Outlook
Looking ahead, the impact of telemetry data is expected to intensify. As industries embrace more automation, interconnected devices, and AI, telemetry will drive predictive maintenance, autonomous systems, and ultra-responsive digital services. The convergence of telemetry with edge computing and 5G will enable broader, faster, and smarter data collection—transforming sectors from smart cities to precision medicine. Privacy, security, and interoperability will remain crucial priorities as the telemetry landscape grows in complexity.
Conclusion
Telemetry data is foundational to modern digital infrastructure, delivering real-time intelligence that powers efficiency, innovation, and safety across countless applications.
[25k5tr]
[21nh1e]
As sensing and connectivity technologies advance, telemetry will continue shaping our world—enabling organizations to anticipate issues, optimize operations, and deliver breakthrough services.
Citations
[25k5tr] 2025, Sep 05. What Is Telemetry Data? Uses, Benefits, & Challenges. Published: 2025-07-17 | Updated: 2025-09-05
[j2l5hd] 2025, Sep 04. What is Telemetry? - Definition, Benefits, & Use Cases. Published: 2024-12-12 | Updated: 2025-09-04
[ltw1qe] 2025, Sep 04. What Is Telemetry Data?. Published: 2025-02-04 | Updated: 2025-09-04
[21nh1e] 2025, Sep 04. What is Telemetry Data?. Published: 2024-08-12 | Updated: 2025-09-04
[fr1ww8] 2025, Sep 05. What is Telemetry Data? How Does It Work, Benefits, .... Published: 2024-06-28 | Updated: 2025-09-05