Internet of Things (IoT)
(2025-09-24T11:45.444Z)
Perplexity Query
(2025-09-24T11:45
.444Z)
Question:
Write a comprehensive one-page article about "Internet of Things".
Model: sonar-pro
A Network of Physical Objects
The Internet of Things (IoT) is a network of physical objects—such as devices, vehicles, appliances, and sensors—embedded with software and connectivity, enabling them to collect and exchange data over the internet.
[v28fze]
[59tg5g]
Its significance lies in the way it transforms routine objects into "smart" systems, allowing for improved automation, efficiency, and real-time decision-making across homes, businesses, and cities.
[v28fze]
[nkzw7k]
In an increasingly connected world, IoT matters because it fundamentally changes how people interact with technology and their environment.
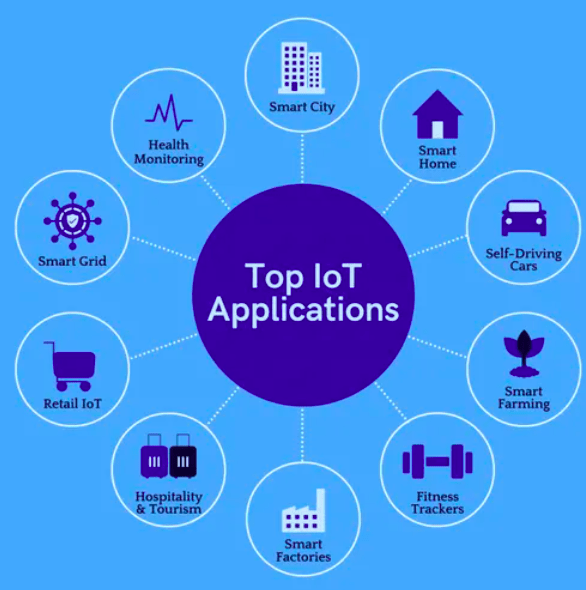
Explaining the Internet of Things
At its core, IoT involves connecting everyday objects to the internet, which enables them to interact, communicate, and perform tasks autonomously.
[59tg5g]
These smart objects can range from simple consumer gadgets, like fitness trackers and smart lighting, to complex machinery and vehicles equipped with multiple sensors.
[v28fze]
Through this network, devices can collect a vast array of data—temperature, air quality, energy usage, movement patterns—and use analytics, artificial intelligence (AI), and machine learning (ML) to interpret and act on this information, often with minimal human intervention.
[nkzw7k]
[59tg5g]
Practical Examples and Use Cases
- Connected Homes: Smart thermostats, lighting systems, and virtual assistants like Alexa or Google Home automate everyday tasks, optimize energy usage, and enhance security. A smart refrigerator can detect depleted groceries and order replacements, while home security systems can alert homeowners about potential threats in real time. [nkzw7k]
Benefits and Potential Applications
IoT offers several benefits:
- Improved Safety and Security: Real-time monitoring enhances security for homes, vehicles, and critical infrastructure, while predictive analytics can prevent accidents and reduce risks. [59tg5g]
Challenges and Considerations
Despite its promise, IoT faces challenges:
- Interoperability: Ensuring different devices and platforms communicate seamlessly is complex, requiring standardization across industries. [59tg5g]
- Scalability and Data Management: The sheer volume of data generated by IoT devices demands robust infrastructure for storage, processing, and analysis, raising concerns over bandwidth and cloud capacity. [59tg5g]
- Regulatory Compliance: Protecting consumer data and meeting legal requirements for data usage and sharing is an ongoing concern. [59tg5g]
Current State and Trends
IoT adoption has accelerated across sectors, with billions of devices now in use worldwide.
[nkzw7k]
[988z7l]
Major technology firms like IBM, Cisco, AWS, and Oracle have developed platforms to support IoT infrastructure, data analytics, and cloud computing.
[v28fze]
[nkzw7k]
[59tg5g]
[d8jl8a]
Key trends include:
- Growth of Industrial IoT (IIoT): Manufacturing, logistics, and utility companies are leveraging IIoT for automation, safety, and asset tracking. IIoT is considered central to the "Industry 4.0" revolution. [59tg5g]
- Integration with AI and ML: IoT systems increasingly use AI and machine learning to interpret sensor data, predict outcomes, and automate responses. [nkzw7k]

Future Outlook
The future of IoT promises faster connectivity (like 5G), smarter AI-driven automation, and deeper integration into every facet of daily life, from personal health to city management.
[nkzw7k]
[59tg5g]
IoT-enabled ecosystems will likely drive new business opportunities, further blur the boundaries between physical and digital experiences, and require ongoing vigilance to address evolving ethical and security concerns.
Conclusion
The Internet of Things is reshaping industries, homes, economies, and societies through unprecedented connectivity and data-driven innovation.
[v28fze]
[nkzw7k]
[59tg5g]
As adoption expands, IoT will continue to unlock new possibilities for intelligent automation and transformative digital experiences, making the world ever more interconnected.
Citations
[v28fze] 2025, Sep 24. What is the Internet of Things (IoT)? - IBM. Published: 2023-05-12 | Updated: 2025-09-24
[nkzw7k] 2025, Sep 24. What is IoT? - Internet of Things Explained - AWS - Updated 2025. Published: 2025-09-23 | Updated: 2025-09-24
[59tg5g] 2025, Sep 24. What Is the Internet of Things? - Oracle. Published: 2024-10-25 | Updated: 2025-09-24
[988z7l] 2025, Sep 24. The Benefits of IoT: Real World Examples | Digi International. Published: 2025-01-30 | Updated: 2025-09-24
[l52hcj] 2025, Sep 24. The Applications of IoT in Business | Tulane University. Published: 2024-08-14 | Updated: 2025-09-24
[d8jl8a] 2025, Sep 23. What Is IoT (Internet of Things)? - Cisco. Published: 2024-08-09 | Updated: 2025-09-23
[7]: 2025, Sep 24. What is the Internet of Things (IoT)? - McKinsey. Published: 2024-05-28 | Updated: 2025-09-24
[8]: 2025, Sep 19. What is the Internet of Things? - DeVry University. Published: 2023-05-13 | Updated: 2025-09-19