Scalable Architecture
(2025-08-17T00:23.525Z)
Perplexity Query
(2025-08-17T00:23
.525Z)
Question:
Write a comprehensive one-page article about "Scalable Software Architecture".
Response from sonar-pro:
Scalable Software Architecture is the design approach that ensures software systems can efficiently handle increasing loads, data volume, and user demand without significant changes to their underlying structure.
[y6d2l7]
[lz4xh8]
This concept is essential for businesses aiming to grow, as good scalability preserves performance, reliability, and user experience even as demands shift rapidly.
[hsehb2]
[mbqoy6]

At its core, scalable software architecture enables systems to grow seamlessly, whether that means accommodating thousands more users, processing larger datasets, or supporting additional features.
[y6d2l7]
The two primary types of scalability are horizontal scaling—adding more servers or machines to distribute the workload—and vertical scaling—upgrading the capacity of current machines.
[y6d2l7]
[lz4xh8]
Both strategies are common: for example, social media platforms like Twitter employ horizontal scaling to manage spikes in user activity during viral events, while financial institutions might use vertical scaling to process increasing transaction volumes without downtime.
Modularity is a fundamental attribute of scalable architectures. Systems are divided into independent components, making it easier to scale or update individual parts without disrupting the whole.
[y6d2l7]
Microservices architecture exemplifies this principle by breaking applications into small, independently-deployable services, each of which can be scaled as needed. For instance, in an e-commerce platform, the product catalog service and the checkout service can be scaled separately depending on usage spikes.
[mbqoy6]
[hsehb2]
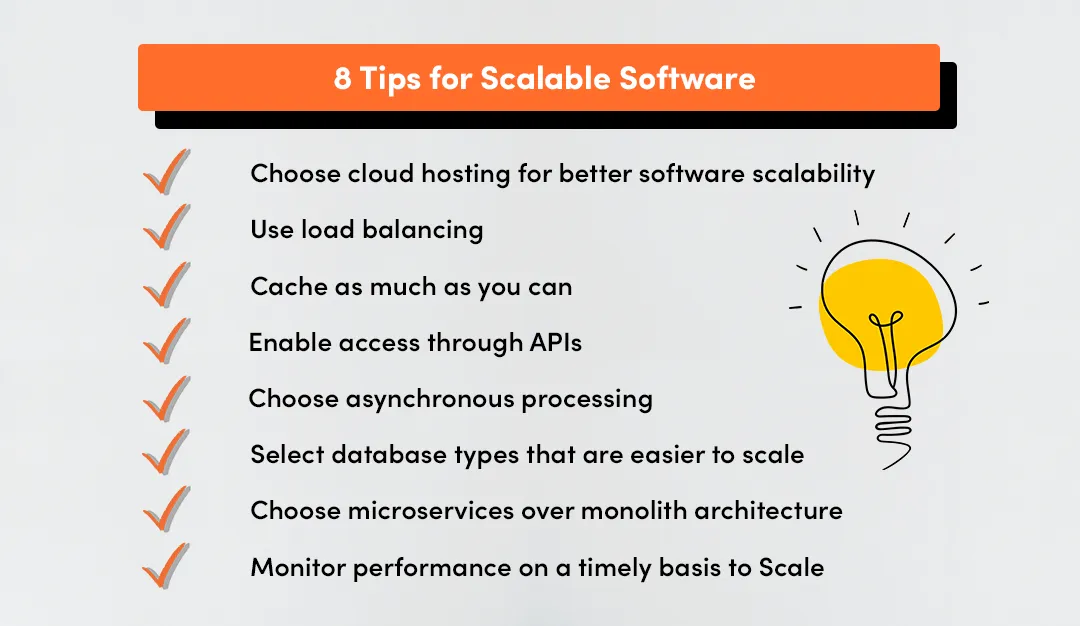
Load Balancing, Caching, and database sharding are critical technical techniques. Load balancing distributes incoming traffic evenly across servers, preventing bottlenecks.
[hsehb2]
[y6d2l7]
Caching stores frequently accessed data closer to the user, reducing load on core databases. Database sharding divides data into smaller pieces stored across multiple machines, allowing faster, parallel access and upgrades.
[hsehb2]
These methods are widely used in industries like online retail, video streaming, and SaaS (Software as a Service), where demand fluctuates and system reliability is crucial.
Practical use cases of scalable software architecture are abundant. Streaming giants like Netflix automatically increase the number of active servers during peak viewing hours to maintain smooth playback for millions of users.
[lz4xh8]
E-commerce firms scale their systems during online sales events, adding infrastructure to handle surges in shoppers.
[6fly3z]
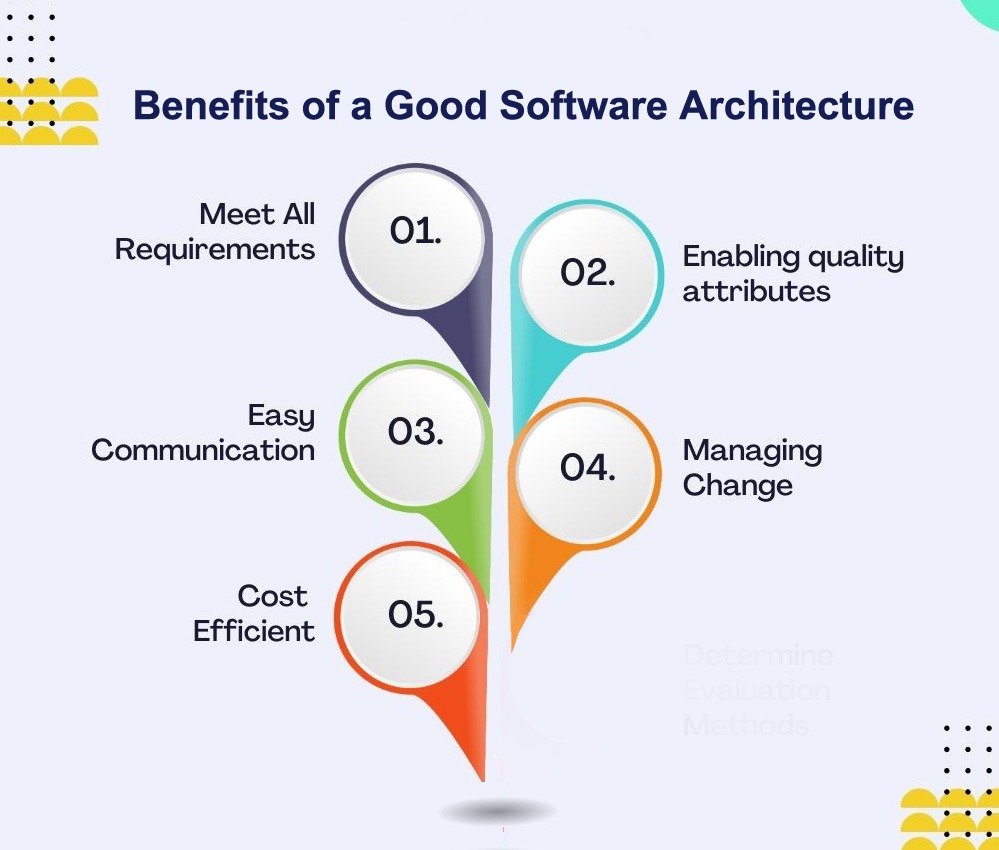
These architectures yield numerous benefits, including improved performance, reduced operational costs, resilience to failures, and agility to add new features or integrate third-party services.
[hsehb2]
[mbqoy6]
[6fly3z]
Despite its power, designing for scalability introduces challenges. Over-engineering can lead to unnecessary complexity and maintainability issues, while underestimating future growth can cause expensive rework or service disruptions.
[hsehb2]
Striking the right balance between flexibility, simplicity, and anticipated demand is a key consideration.
[hsehb2]
Currently, scalable software architecture is the industry standard, especially among high-growth companies and those migrating to cloud platforms.
[lz4xh8]
Major technology providers—Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, Google Cloud, and others—offer robust infrastructure and tools for scalable deployments, such as auto-scaling groups, container orchestration through Kubernetes, and serverless computing.
[lz4xh8]
Microservices, containerization (e.g., Docker), and Infrastructure-as-Code tools (e.g., Terraform) are now mainstream, accelerating adoption and lowering barriers to entry.
[lz4xh8]
[mbqoy6]
Market leaders across sectors rely on scalable architectures to remain competitive. Recent advancements like serverless computing, event-driven architectures, and edge computing further enhance flexibility and responsiveness, making real-time scalability accessible for smaller businesses.
[y6d2l7]
[lz4xh8]
Companies are increasingly embracing DevOps and CI/CD pipelines to ensure rapid, reliable scaling of both infrastructure and software.
Looking forward, scalable software architecture will be central to the growth of areas such as artificial intelligence, IoT (Internet of Things), and global distributed applications. Automation, predictive scaling, and increased adoption of cloud-native and edge-first patterns are expected. As digital transformation continues, this architecture will increasingly shape how organizations respond to unpredictable demand, build resilient systems, and compete in dynamic markets.
In summary, scalable software architecture is fundamental for future-proofing modern digital systems, driving performance, reliability, and innovation. As businesses and technologies evolve, the ability to scale seamlessly will remain a decisive factor for long-term success.
Citations
[hsehb2] 2025, May 02. Benefits of Scalable Software Architecture for Business .... Published: 2024-03-25 | Updated: 2025-05-02
[mbqoy6] 2025, Aug 13. Scalable Software: Why It's Crucial for Future-Proofing .... Published: 2024-08-19 | Updated: 2025-08-13
[6fly3z] 2025, Jun 16. Scalable Architecture Patterns for High-Growth Startups .... Published: 2025-04-09 | Updated: 2025-06-16
[y6d2l7] 2025, Mar 09. Mastering Scalable Software Architecture: Key Insights. Published: 2024-10-31 | Updated: 2025-03-09
[lz4xh8] 2025, Jun 16. Scalable Architecture: A Definition and How-To Guide. Published: 2021-05-04 | Updated: 2025-06-16