Continuous Refactoring
Continuous Rewrites
(2025-08-15T09:28.338Z)
Perplexity Query
(2025-08-15T09:28
.338Z)
Question:
Please describe the best-practice but often ignored principle of "Continuous Refactoring" in developing modern software.
Response from sonar-pro:
Continuous Refactoring is the disciplined practice of improving and tidying up code regularly—not as a one-off task, but as a continuous activity throughout the software development lifecycle. Although recognized as a best practice, it is frequently neglected due to short-term deadlines or the mistaken belief that refactoring is only necessary when problems become visible.
_
What is Continuous Refactoring?
- Continuous refactoring means integrating small-scale code improvements into your daily development routine, preventing the accumulation of Technical Debt (inefficient, difficult-to-maintain code) and avoiding the need for risky, large-scale rewrites later on [5zfhvz] [s7b4dn] .
- Proper continuous refactoring is inseparable from automated testing: robust unit and integration tests ensure changes do not break existing features [s7b4dn] .
Why is Continuous Refactoring Important?
Best-Practice Principles (Often Ignored):
| Principle | Why It's Important | Typical Reason Ignored |
| Refactor as you go | Prevents large rewrites, keeps code quality high | Pressure to deliver features fast, de-prioritizing cleanup |
| Commit small, commit often | Makes problems easier to isolate, simpler rollbacks | Belief that only "big changes" are worth pushing |
| Write and run tests before refactoring | Ensures refactoring is safe and doesn’t break code | Lack of tests; pressure to skip to "just work" |
| Reduce the need for massive refactors | Good planning and conventions limit future issues | Many teams skip this step in the rush to start coding [5zfhvz] [s7b4dn] |
| Focus on code “smells” and structure | Early detection of problems avoids complexity | Teams ignore signs, only fixing “broken” code |
| Share and discuss refactoring plans | Makes continuous improvement a team effort [95z9nz] | Developers refactor in isolation, risking merge conflicts, confusion |
| List and schedule deferred refactorings | Important issues not lost, shared team awareness | Many ignore or never communicate improvements for later [95z9nz] |
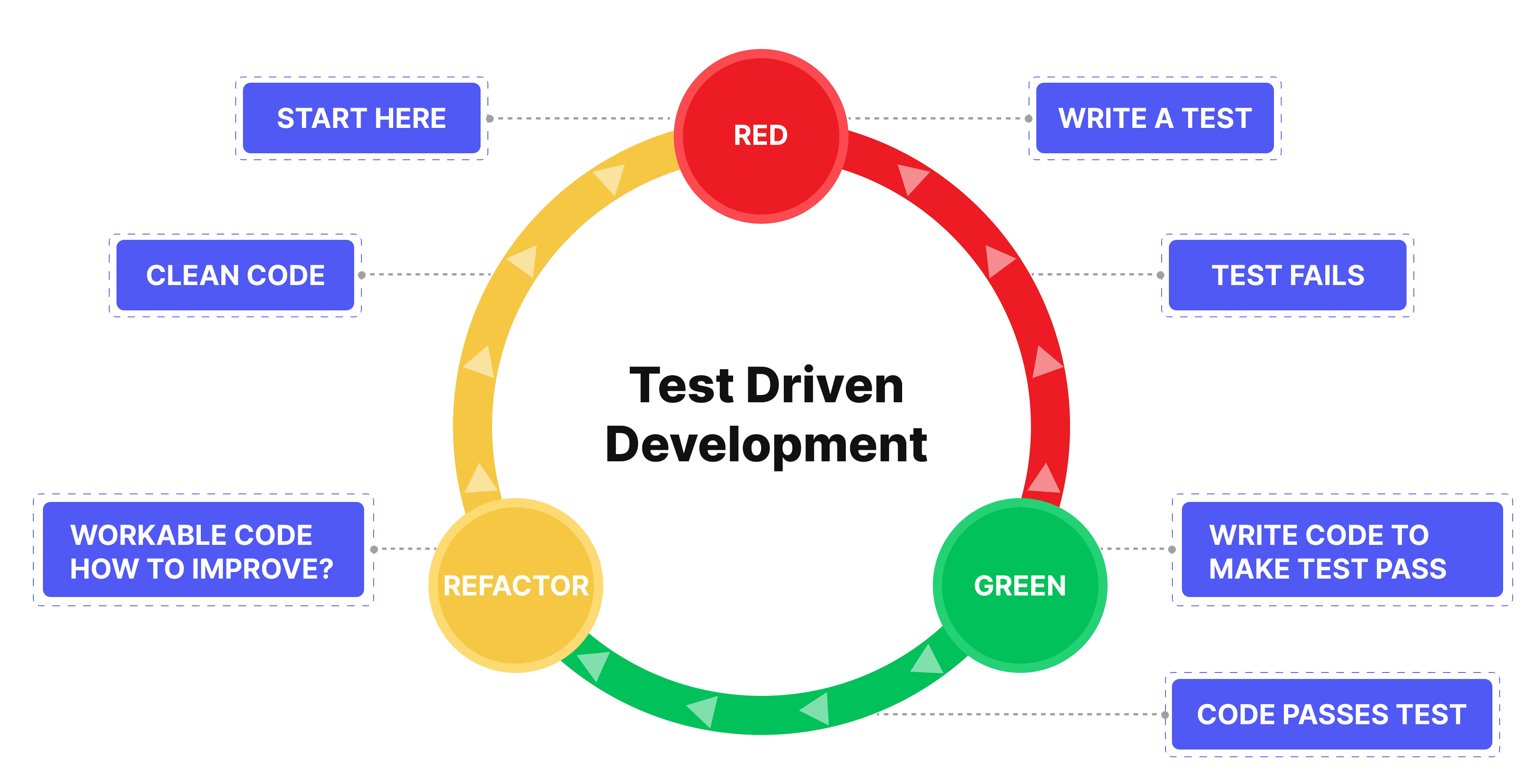 Imagine a diagram showing the software development process as a continuous loop: "Code → Refactor → Test → Deploy → Repeat." This loop emphasizes that refactoring is part of every cycle, not a separate or final phase.
Imagine a diagram showing the software development process as a continuous loop: "Code → Refactor → Test → Deploy → Repeat." This loop emphasizes that refactoring is part of every cycle, not a separate or final phase.Practical Example
Suppose a developer spots a large function performing multiple unrelated tasks while fixing a bug. Instead of ignoring it to save time, they extract each logical segment into smaller, single-purpose functions and run existing tests to ensure nothing breaks. This small but continuous effort ensures the code stays readable and flexible for future changes
[xjbd35]
[27gl6k]
[s7b4dn]
.
 Visual: Before/after refactoring a "God function" into three smaller, named functions, annotated with a checklist showing reduced complexity and improved test coverage.
Visual: Before/after refactoring a "God function" into three smaller, named functions, annotated with a checklist showing reduced complexity and improved test coverage.Common Barriers and Solutions
 Visual: Pie chart or infographic showing that projects with regular refactoring have fewer defects and faster feature integration compared to projects that defer refactoring.
Visual: Pie chart or infographic showing that projects with regular refactoring have fewer defects and faster feature integration compared to projects that defer refactoring.Summary of Key Habits for Continuous Refactoring
- Keep changes frequent and small.
- Always maintain or add tests before and after refactoring.
- Encourage team-wide conventions and open discussion of needed improvements.
- Document any deferred refactoring tasks and schedule them as part of the development cycle [95z9nz] .
Continuous refactoring is one of the most impactful, yet overlooked disciplines in professional software development—best adopted not as a one-off event, but as an ongoing team habit, integrated into every sprint and commit
[5zfhvz]
[95z9nz]
[s7b4dn]
.
Citations
[5zfhvz] 2025, Jun 25. Continuous refactoring: avoiding technical debt in the here and now. Published: 2019-02-01 | Updated: 2025-06-25
[95z9nz] 2024, Dec 10. Continuous Refactoring - Codit. Published: 2017-02-28 | Updated: 2024-12-10
[xjbd35] 2025, Aug 14. 6 Code Refactoring Best Practices - Mad Devs. Published: 2024-05-07 | Updated: 2025-08-14
[27gl6k] 2025, Jun 16. clean your code - Refactoring.Guru. Published: 2014-01-01 | Updated: 2025-06-16
[s7b4dn] 2024, Jul 30. Continuous Refactoring. 12 Best Practices from Ruby Developers. Published: 2023-10-25 | Updated: 2024-07-30