Apache Spark
(2025-11-23T18:58.418Z)
Perplexity Query
(2025-11-23T18:58
.418Z)
Question:
Write a comprehensive one-page article about "Apache Spark".
Model: sonar-pro
An open-source analytics engine designed for large-scale data processing
Apache Spark is an open-source analytics engine designed for large-scale data processing, offering lightning-fast performance and unified support for batch and real-time analytics[3][4][5]. Its ability to handle vast datasets across distributed clusters makes it critical for modern data engineering, machine learning, and business intelligence applications.
Spark matters in today’s digital economy because organizations need to extract insights from massive, complex data sources quickly. Traditional processing tools are often slow or inflexible; Spark addresses these challenges by enabling high-speed, scalable analytics that power AI, personalization, predictive modeling, and more[2][4].

Main Content
Architecture and Core ConceptsAt the heart of Apache Spark’s speed and fault tolerance is its use of Resilient Distributed Datasets (RDDs), which distribute data across clusters and enable in-memory processing[1][3][4]. The foundational Spark Core engine provides essential services like task scheduling, memory management, and job execution. Key architectural components include the Spark Driver, which manages job scheduling through directed acyclic graphs (DAGs), and the SparkContext, which initializes and coordinates cluster resources and data manipulations[1][2][6].
Practical Examples and Use Cases
- Data transformation and ETL: Spark is widely used for Extract, Transform, Load (ETL) pipelines, enabling efficient processing of log files, sensor data, or social media streams.
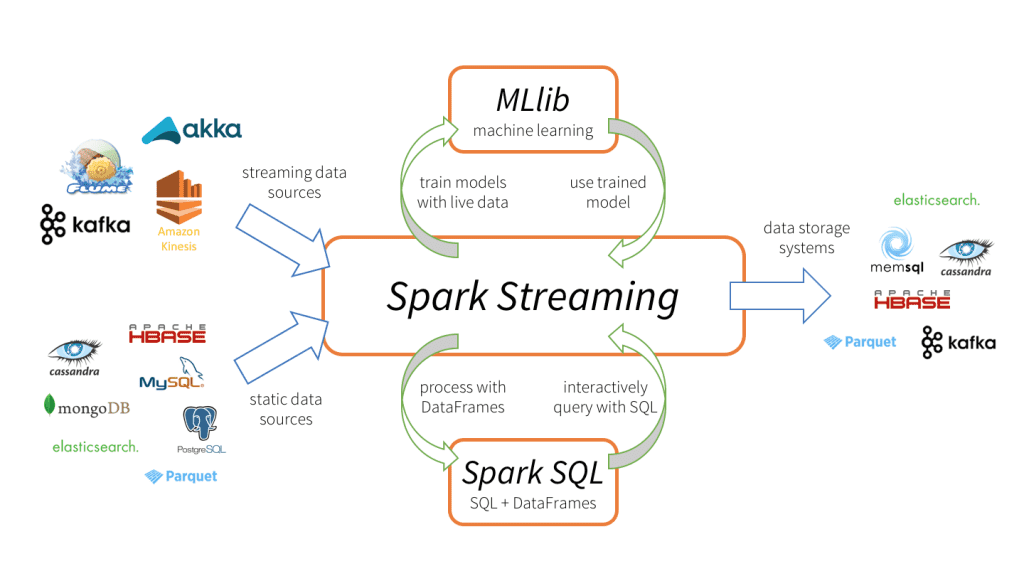
- Real-time analytics: With Spark Streaming, organizations analyze live financial transactions for fraud detection or monitor IoT device streams for predictive maintenance[2][3].
- Machine learning: Spark’s MLlib library facilitates large-scale training of models for recommendation systems, customer segmentation, or anomaly detection[5].
- Interactive data exploration: Data scientists leverage Spark SQL for ad-hoc queries on massive datasets, powering dashboards and business insights[3].
Benefits and Potential Applications
- Speed: Thanks to in-memory computing, Spark can process data up to 100x faster than traditional disk-based frameworks like Hadoop MapReduce[2][3][4].
- Unified platform: Spark supports batch, streaming, SQL, machine learning, and graph processing through a common API, simplifying complex data workflows[3][8].
- Scalability: Spark can scale to thousands of nodes, accommodating petabyte-scale data[2].
- Ease of use: High-level APIs exist for Python, Java, Scala, and R, making Spark accessible to a wide range of developers and analysts[1][2].
Challenges and ConsiderationsDespite its strengths, Spark requires careful cluster management and memory optimization, especially for truly massive datasets that may not fit in RAM. As workloads scale, Spark’s speed advantage can diminish, and operational complexity or costs become factors to address[2]. Integration with existing systems and security in multi-tenant environments are also important considerations.

Current State and Trends
Apache Spark is now an industry-standard platform, widely adopted by tech leaders such as Databricks, IBM, and cloud providers like Microsoft Azure and Google Cloud[3][4][6][8]. Major enterprises use Spark to power recommendation systems, real-time fraud analytics, and large-scale genomic research. The ecosystem includes key libraries: Spark SQL, Spark Streaming, MLlib (machine learning), and GraphX (graph processing)[3][5].
Recent trends involve tighter integration with cloud services, Kubernetes support for dynamic cluster management, and acceleration via GPUs and FPGAs[4]. Spark’s Dataframe and Dataset APIs have become dominant for higher-level abstractions and performance tunings[5].
Future Outlook
As data volumes and AI adoption accelerate, Apache Spark is expected to remain central to advanced analytics infrastructure. Innovations in hardware acceleration, smarter resource management, and improved APIs will allow Spark to handle greater scale and more complex workflows. Its integration with cloud-native tools and streaming platforms will further expand use cases, shaping next-generation data-driven applications in healthcare, finance, and beyond[4].
Apache Spark has redefined the possibilities of big data analytics with its speed, scalability, and versatility. As organizations deepen their reliance on data, Spark’s continuing evolution will help unlock new insights, driving innovation well into the future.
Citations
[1]: 2025, Nov 23. Apache Spark architecture: Concepts, components, and best practices. Published: 2025-10-29 | Updated: 2025-11-23
[2]: 2025, Nov 22. What is Apache Spark? A Complete Guide - Codecademy. Published: 2025-07-31 | Updated: 2025-11-22
[3]: 2025, Nov 22. Introduction to Apache Spark - Databricks. Published: 2025-11-13 | Updated: 2025-11-22
[6]: 2025, Oct 11. Apache Spark in Azure Synapse Analytics overview - Microsoft Learn. Published: 2024-11-08 | Updated: 2025-10-11
[7]: 2025, Nov 08. Apache Spark™ - Unified Engine for large-scale data analytics. Updated: 2025-11-08
[8]: 2025, Nov 23. What is Apache Spark? | Google Cloud. Published: 2025-11-21 | Updated: 2025-11-23
