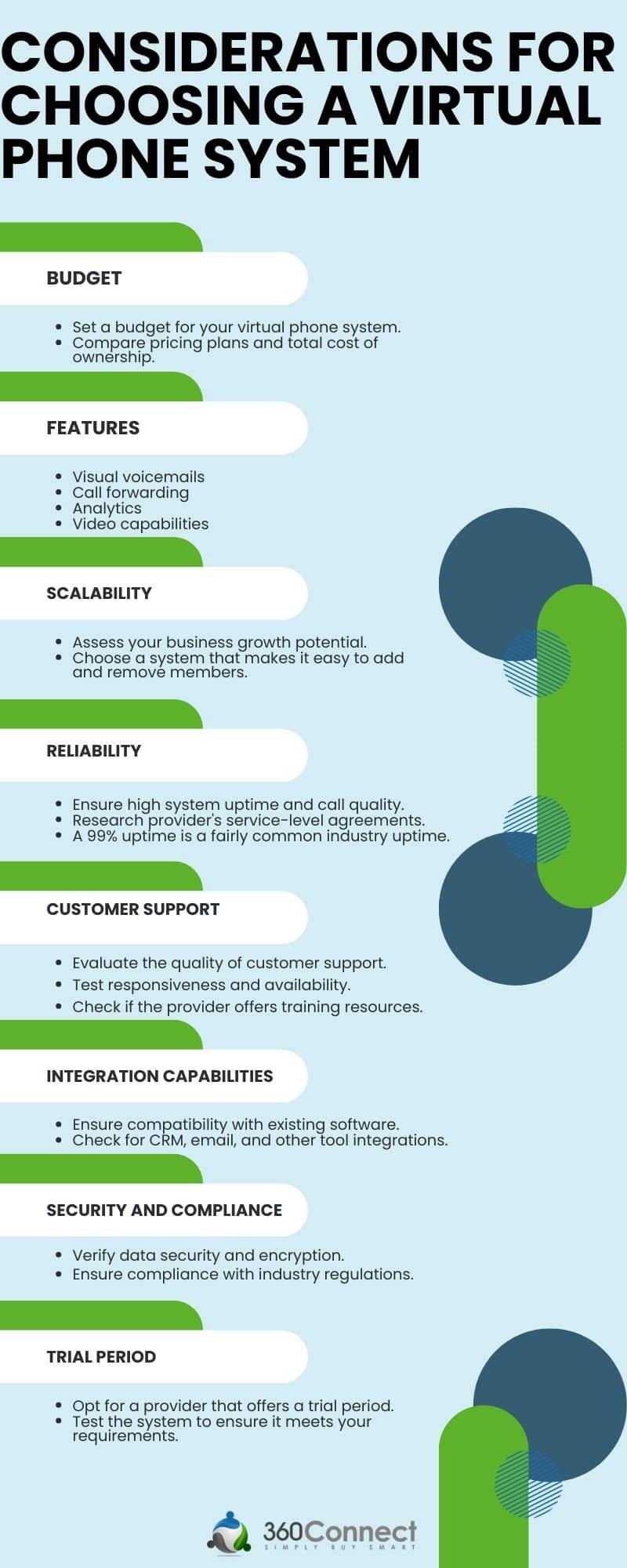
Virtual Phone Systems
A virtual phone system is a cloud-based communication platform that enables individuals and businesses to make and receive calls over the internet rather than through traditional landlines or on-premises private branch exchange (PBX) systems. This technology has become increasingly significant as remote work and global business operations demand cost-effective, flexible, and scalable communication solutions.

At its core, a virtual phone system operates by routing calls using Voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP), allowing users to handle phone communications from computers, smartphones, or IP-enabled desk phones. Unlike legacy setups, which require expensive hardware and complex installation, virtual systems are managed via web interfaces and require little more than a stable internet connection and a device. For example, a small business can use a virtual phone system to assign a professional business number to staff working from multiple locations, with features such as automated call attendants, call forwarding, voicemail-to-email, and even SMS messaging built in [1][4].


Practical applications are wide-ranging. A startup might use a virtual phone system to present a unified national presence, automatically routing calls to sales agents wherever they are. Customer service teams benefit from advanced call routing and analytics tools that make it possible to track, record, and optimize every customer interaction. Many virtual phone systems also integrate seamlessly with popular customer relationship management (CRM) tools, further streamlining business operations [2].
Among the primary advantages are cost savings, since there is no need to purchase or maintain physical phone infrastructure. Businesses pay only for the features and virtual lines they use, and international calling costs are often much lower than with traditional networks [1][3]. Virtual phone systems excel in scalability—new lines, users, or features can be added at the click of a button, which is especially beneficial for rapidly growing companies or those with seasonal fluctuations in demand. Furthermore, remote access capabilities mean that employees can operate efficiently from any location, with mobile and desktop apps supporting a distributed workforce [4][5].
However, there are important considerations. Call quality and reliability are dependent on internet connectivity, so insufficient bandwidth or unstable networks can degrade the user experience. Security is also a concern, although most reputable providers implement strong encryption and compliance protocols to protect sensitive information. Occasionally, complex regulatory requirements for emergency call routing (E911) or local number portability may need specialized setup.
The adoption of virtual phone systems has grown rapidly, fueled by the expansion of remote and hybrid work models and the need for businesses to remain agile and responsive across locations. Major providers such as RingCentral, CloudTalk, Ooma, Grasshopper, and CallRail have led the market by offering intuitive platforms with a wide range of features designed for teams of all sizes [3][4][5]. Recent advances include AI-driven call analytics, transcription services, and integration with next-generation collaboration tools to further enhance productivity and customer engagement [1].
As the market evolves, trends point toward even greater automation, with artificial intelligence used to route calls more intelligently and analyze spoken interactions for improved service. Providers continue to invest in better security, more seamless integrations, and user-friendly interfaces to remove barriers to adoption for organizations of any size. The sector remains highly competitive, driving continuous innovation and a focus on user experience.
Looking ahead, the future of virtual phone systems is poised for further transformation as 5G and high-speed internet become ubiquitous, making high-definition voice and integrated video communication standard. Enhanced AI features may soon automate more of the customer service process, provide real-time insights during calls, and predict call outcomes. As more businesses prioritize flexibility and digital transformation, virtual phone systems are likely to become the backbone of modern business communication infrastructure.

Virtual phone systems offer an affordable, flexible, and future-ready solution to today’s communication needs. As technology continues to evolve, these systems will play an increasingly vital role in enabling seamless, global connectivity for businesses and individuals alike.
The most innovative providers of virtual phone services as of 2025 are generally recognized as Nextiva, RingCentral, Dialpad, Zoom Phone, Phone.com, Grasshopper, and Ooma. These companies distinguish themselves with advanced integrations, AI-powered features, and adaptability across business sizes and sectors. Here is a breakdown of their innovation, stage, and supporting details:
1. Nextiva
- Innovation: Advanced call routing, voicemail-to-email, AI-powered automation, robust CRM/help desk integrations, and strong call analytics. Noted for high reliability and ease of setup, suitable for both small businesses and scaling teams (WPBeginner).
- Stage: Growth/Mature. Founded in 2006, Nextiva has established itself as a leading cloud communications company with a strong market presence and significant client base (WPBeginner).
 : An illustration of how Nextiva integrates with multiple business apps to streamline communication could visualize this innovation.
: An illustration of how Nextiva integrates with multiple business apps to streamline communication could visualize this innovation.
2. RingCentral
- Innovation: Notable for AI-powered call transcriptions, video meeting summaries, over 400 integrations (including Google Workspace and Microsoft), APIs for custom workflow automation, and a powerful group chat with chatbot automation (CyberNews).
- Stage: Mature. RingCentral is publicly traded (NYSE: RNG) and a long-established VoIP leader since 1999, continually innovating with AI and global capabilities (CyberNews, TechnologyAdvice).
3. Dialpad
- Innovation: AI-driven voice intelligence for real-time transcription and sentiment analysis, seamless app integrations, and focus on remote collaboration (CyberNews).
- Stage: Growth. Founded in 2011, Dialpad has rapidly expanded and raised significant funding, with increasing market adoption but not yet a public company (CyberNews).
4. Zoom Phone
- Innovation: Unified communications platform integrating voice, video, and messaging; renowned for easy scaling and integration with Zoom meetings for hybrid/remote teams (TechnologyAdvice, WPBeginner).
- Stage: Mature (as part of Zoom). Launched as an extension of Zoom Video Communications, Zoom Phone builds on Zoom’s established infrastructure.
5. Phone.com
- Innovation: Flexible vanity phone number services, powerful automated attendants with Interactive Voice Response, extensive call management, and customizable extensions (VoIPReview).
- Stage: Growth/Mature. Founded in 2007, Phone.com has sustained growth and stabilized within the SMB segment (VoIPReview).
6. Grasshopper
- Innovation: Focused on virtual numbers for solopreneurs and small businesses; streamlined setup, mobile-centric, affordable with strong SMS and voicemail capabilities (TechnologyAdvice).
- Stage: Mature. Established in 2003 and acquired by LogMeIn, Grasshopper serves a niche but robust sector.
7. Ooma
- Innovation: Exceptional home office integration, simple VoIP hardware, feature-rich mobile/desktop applications (TechnologyAdvice).
- Stage: Mature. Publicly traded and widely adopted by residential and business users.
Citations: