Unstructured Data
(2025-09-20T14:45.774Z)
Perplexity Query
(2025-09-20T14:45
.774Z)
Question:
Write a comprehensive one-page article about "Unstructured Data".
Model: sonar-pro
Unstructured Data: Unlocking Insights Beyond Databases
Unstructured data refers to information that lacks a predefined model or consistent format, making it distinct from neatly-organized tables or databases. It is significant because the vast majority of information created today—such as emails, images, social media posts, and videos—falls into this category, containing valuable insights that are challenging to extract using traditional data analysis techniques.
[i42tx6]
[x41p0i]
[5eff28]
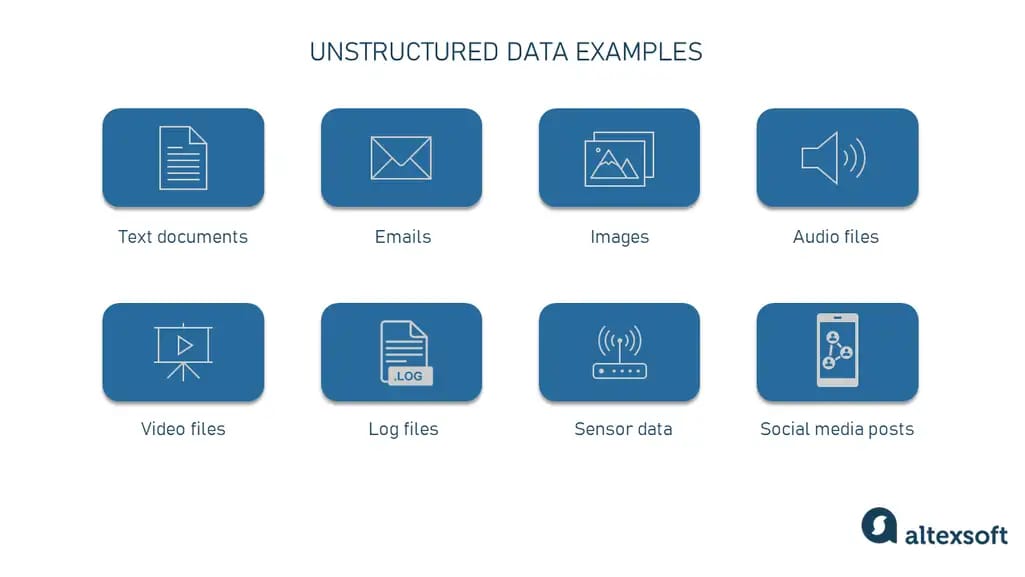
Understanding Unstructured Data
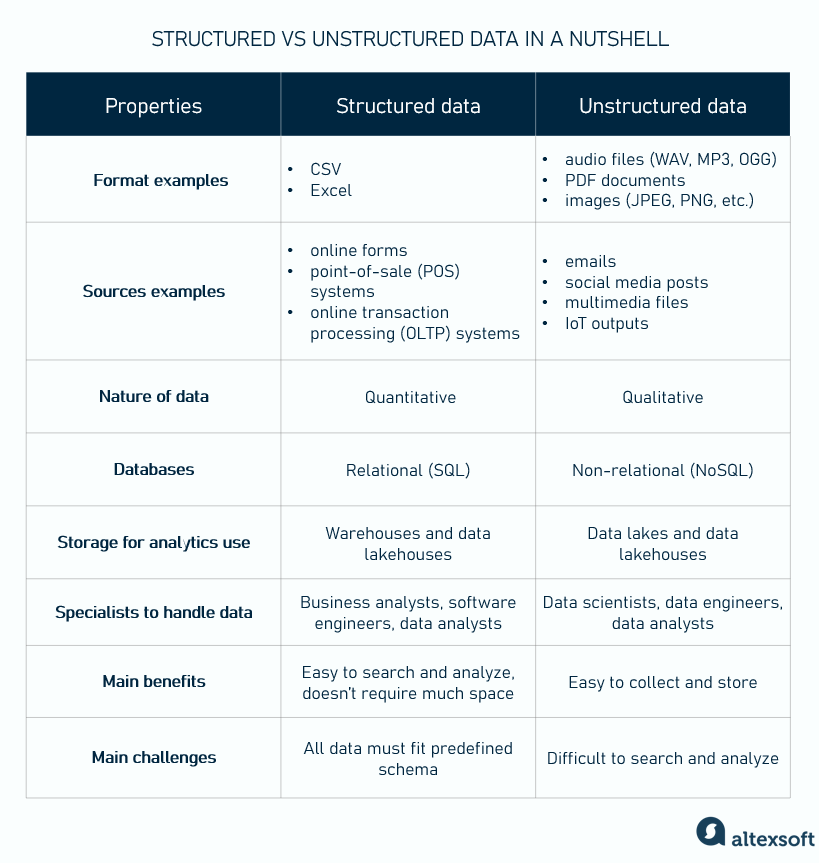
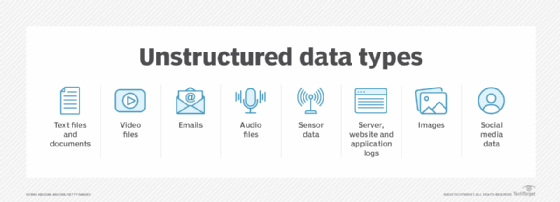
Unstructured data encompasses a wide variety of content types. Unlike structured data, which fits neatly into rows and columns (think spreadsheets with specific fields), unstructured data is messy, diverse, and often stored in its original format. Formats include text documents (emails, PDF files, presentations), multimedia files (photos, audio recordings, videos), and digital communications found throughout social media platforms (posts, comments, tweets).
[i42tx6]
[x41p0i]
[ajmv9o]
[5eff28]
For example:
- A company’s customer service department receives millions of emails, chat logs, and recorded phone calls each year. Each of these records varies in content, style, and length, and doesn't fit neatly into a fixed template.
- Sensor data from IoT (Internet of Things) devices, such as logs from manufacturing equipment, is mostly unstructured though it contains operational insights. [x41p0i]
Handling unstructured data requires specialized tools and techniques, such as natural language processing (NLP), sentiment analysis, and machine learning algorithms, which can process large amounts of diverse, unsorted information and extract meaningful patterns or trends.
[ajmv9o]
[5eff28]
Benefits and Applications
The true value of unstructured data emerges when organizations harness it to gain a deeper understanding of their business environment and customers. Practical applications include:
- Market intelligence: Analyzing online reviews or social media conversations to gauge public perception of products.
- Healthcare: Extracting insights from doctors’ notes, medical imaging, or recorded consultations for improved diagnostics.
- Security: Identifying suspicious activity by analyzing logs, emails, and surveillance footage.
Despite its promise, unstructured data presents significant challenges. Its sheer volume and lack of organization complicate storage, retrieval, and analysis. Advanced hardware, sophisticated software, and specialized skills are required to process and interpret this data. Privacy, data security, and compliance issues also arise when handling sensitive information within unstructured content.
[i42tx6]
[ajmv9o]
[5eff28]
Current State and Trends
The digital universe is experiencing exponential growth in unstructured data—by some estimates, unstructured data now represents more than 85% of all business information.
[i42tx6]
Major technology players have responded with purpose-built tools and platforms, such as Apache Hadoop, Amazon S3, Microsoft Azure Blob Storage, and Google Cloud Storage, which are designed to ingest, process, and analyze diverse data types efficiently.
[x41p0i]
[ajmv9o]
Artificial intelligence (AI), particularly machine learning and deep learning, is increasingly used to automate the categorization and extraction of insights from unstructured sources like text, images, and audio. The rise of natural language processing and computer vision technologies has enabled applications such as chatbots, sentiment analysis engines, and image classifiers.
Future Outlook
As tools become more powerful and accessible, and as data privacy frameworks evolve, organizations will increasingly rely on unstructured data analysis for strategic decision-making and automation. Future developments will likely include more advanced AI models capable of understanding context, emotion, and intent in complex data, ushering in breakthroughs for industries ranging from healthcare to entertainment and beyond.
Conclusion
Unstructured data is both a challenge and an opportunity—representing the majority of the world’s information and offering untapped insights for those equipped to interpret it.
[i42tx6]
[x41p0i]
[5eff28]
As analytic technologies continue to advance, the ability to unlock the value hidden within unstructured data will define tomorrow’s leaders in business and science.
Citations
[i42tx6] 2025, Sep 08. Glossary: Unstructured Data | resources.data.gov. Published: 2002-01-01 | Updated: 2025-09-08
[x41p0i] 2025, Sep 08. What is unstructured data? | Definition from TechTarget. Published: 2025-03-14 | Updated: 2025-09-08
[ajmv9o] 2025, Sep 20. Structured vs Unstructured Data Explained with Examples - AltexSoft. Published: 2024-12-16 | Updated: 2025-09-20
[5eff28] 2025, Sep 20. What is Unstructured Data? - GeeksforGeeks. Published: 2025-06-24 | Updated: 2025-09-20
[6]: 2025, Sep 20. Examples of Unstructured Data - MongoDB. Published: 2025-04-02 | Updated: 2025-09-20
[7]: 2025, Sep 20. Structured vs. Unstructured Data: What's the Difference? - IBM. Published: 2025-02-07 | Updated: 2025-09-20
[8]: 2025, Sep 20. What is Unstructured Data with Examples? : Explained - Securiti.ai. Published: 2024-10-01 | Updated: 2025-09-20
[9]: 2025, Sep 20. Structured Data vs Unstructured Data - Difference Between ... - AWS. Published: 2025-09-02 | Updated: 2025-09-20