Thought Control
(2025-08-16T22:44.115Z)
Perplexity Query
(2025-08-16T22:44
.115Z)
Question:
What is "Thought Control" in training large scale reasoning models?
Response from sonar-pro:
"Thought Control" in training large-scale reasoning models refers to techniques and mechanisms that explicitly guide, supervise, or constrain the internal step-by-step reasoning processes these models use to solve complex problems, often to ensure accuracy, transparency, and reliability in their outputs.
Large language models (LLMs) with reasoning abilities differ from traditional models by employing structured, stepwise problem-solving known as chain-of-thought (CoT) reasoning.
[55umht]
[u30x80]
[pkp99o]
Instead of jumping straight to an answer, these models break questions into smaller sub-steps—often called reasoning traces—and work through each intermediate decision before producing the final answer.
[55umht]
[u30x80]
[pkp99o]
Thought control addresses challenges associated with this multi-step reasoning by:
- Supervising or constraining each intermediate step in the model’s thought process, ensuring logical consistency and minimizing “hallucinations.”
- Allowing researchers or engineers to prompt or direct the model towards particular styles of intermediate reasoning, often through engineered prompts or specialized training objectives.
Essential Context & Supporting Details
- Reasoning-based-Models “think before speaking”: Unlike traditional generation, reasoning models generate multiple steps and check their logic, similar to internal monologue or “metacognition” in humans. [55umht] [u30x80] [pkp99o]
- Chain of Thought supervision is commonly used: during training, models are shown not only the correct answer but the correct sequence of reasoning steps, and are penalized for wandering off logical paths. [55umht] [u30x80]
- Practical advantages: Thought control increases the transparency of model decisions, facilitates debugging, and helps ensure that models follow domain-specific rules or regulations. [u30x80]
Visual Aids & Examples
 **Visualizes the difference between a classic direct-answer LLM and a reasoning model with CoT and thought control:
**Visualizes the difference between a classic direct-answer LLM and a reasoning model with CoT and thought control:- The reasoning model generates a sequence: step 1 → step 2 → … → answer, with supervision at each step.
 Shows how, in tasks like math or scientific reasoning, a model under thought control spells out each calculation or logical move before reaching the result, with real-time evaluation or correction.
Shows how, in tasks like math or scientific reasoning, a model under thought control spells out each calculation or logical move before reaching the result, with real-time evaluation or correction.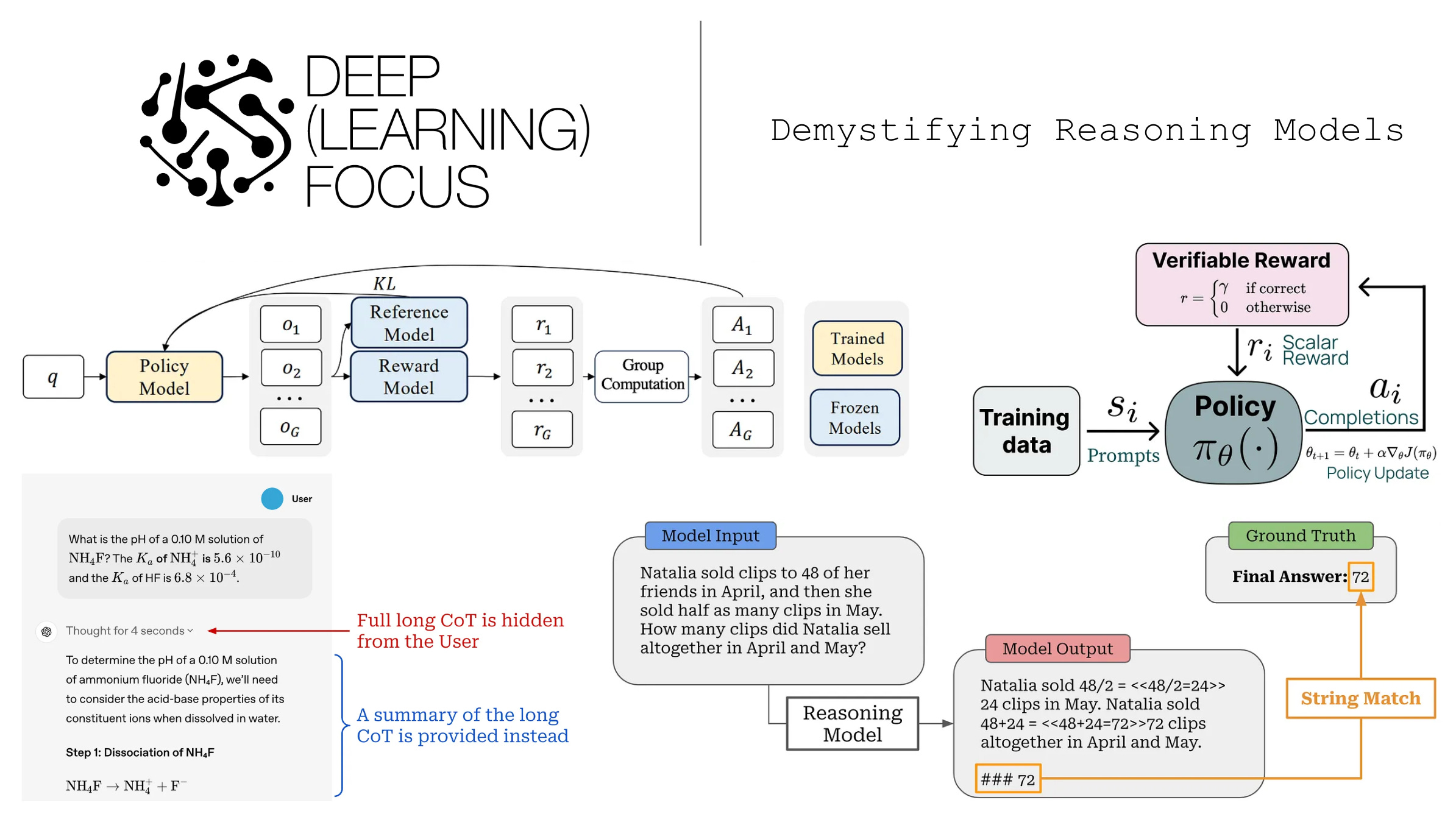 Depicts mechanisms like reinforcement learning from human feedback (RLHF) or expert-written chain-of-thought exemplars, demonstrating how stepwise supervision enforces high-quality reasoning paths.
Depicts mechanisms like reinforcement learning from human feedback (RLHF) or expert-written chain-of-thought exemplars, demonstrating how stepwise supervision enforces high-quality reasoning paths.
Further Considerations
- Overuse of anthropomorphic metaphors like “thought process” or “thinking” is a convenience; reasoning models do not possess consciousness but follow algorithmic patterns enforced by their training data and supervision regimes. [u30x80]
- Thought control is an active research area, especially as models scale in complexity, with ongoing study into the best ways to achieve robust, controllable, and generalizable reasoning. [u30x80]
In summary, thought control in large-scale reasoning models refers to the set of training and inference strategies that keep their “thinking” logical, transparent, and aligned with human reasoning standards—vital for deploying these systems safely and effectively in the real world.
[55umht]
[u30x80]
[pkp99o]
Citations
[55umht] 2025, Jun 26. Demystifying Reasoning Models: How AI Learns to “Think” Step-by .... Published: 2025-06-25 | Updated: 2025-06-26
[u30x80] 2025, Aug 07. What Is a Reasoning Model? | IBM. Published: 2025-08-07 | Updated: 2025-08-07
[pkp99o] 2025, Jun 16. What is AI Reasoning? | NVIDIA Glossary. Published: 2025-05-29 | Updated: 2025-06-16
[5]: 2025, Aug 13. What is AI Reasoning? Key Types and Applications in 2025 - Aisera. Published: 2025-08-13 | Updated: 2025-08-13