Support Vector Machines
(2025-11-11T15:03.183Z)
Perplexity Query
(2025-11-11T15:03
.183Z)
Question:
What are Support Vector Machines in Data Science? When are they used properly? What are alternatives? How can they help companies improve how they use data?
Model: sonar-pro
Support Vector Machines (SVMs) are supervised machine learning algorithms widely used for both classification and regression tasks in data science, with particular strength in finding an optimal boundary (hyperplane) to separate different classes within a dataset.
[3lp9q7]
[gb1ju5]
[10wu6s]
Key Concepts and How SVMs Work
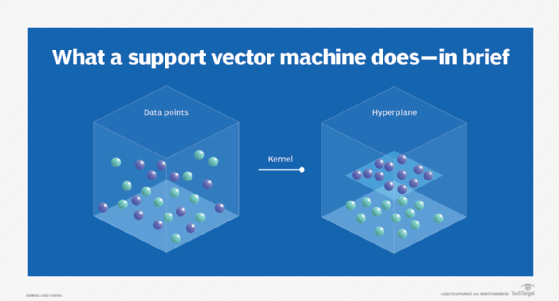
- Hyperplane: The core function of an SVM is to find a hyperplane in the feature space that best separates classes. For two-dimensional data, this appears as a line; for higher dimensions, it becomes a plane or higher-dimensional space. [3lp9q7] [gb1ju5]
 Imagine two groups of data points (e.g., circles and squares) on a plane—the SVM determines the line (hyperplane) that best separates these groups.
Imagine two groups of data points (e.g., circles and squares) on a plane—the SVM determines the line (hyperplane) that best separates these groups.
Proper Usage of SVMs
SVMs are typically used when:
- The dataset is moderately sized; SVMs can be less efficient with extremely large datasets.
- Data classes are clearly distinguishable, or separable with non-linear kernels.
- Robustness to outliers is needed, as SVMs tend to ignore non-critical outliers. [3lp9q7]
Alternatives to SVMs
Common alternatives include:
| Algorithm | Best Use Cases |
| Logistic Regression | Linearly separable data, probabilistic output |
| Decision Trees | Interpretable models, non-linear relationships |
| Random Forests | Large, complex datasets with mixed data types |
| Neural Networks | Very large datasets, complex feature interactions |
| k-Nearest Neighbors | Simple, non-parametric, proximity-based analysis |
| Naive Bayes | High-dimensional, independent feature assumptions |
 |
Alternatives may be preferred when a dataset is enormous, features are highly correlated, or interpretability is crucial.
How SVMs Help Companies Use Data More Effectively
- Handling Complex Relationships: Kernels enable SVMs to model complex, non-linear boundaries, allowing companies to extract value from unstructured or non-linearly separable data types (e.g., images, text).
- Data-Driven Insights: When properly tuned, SVMs enable more actionable business intelligence, making sense of data patterns that might be missed by simpler models.
In summary, SVMs provide companies with sophisticated and accurate tools for data-driven decision-making where separating classes and identifying clear boundaries in data is essential. Their utility is highest where robustness, flexibility, and precision are required, though consideration of sample size and computational cost is necessary when choosing among alternatives.
[3lp9q7]
[1rfn6v]
[4zeqh9]
Citations
[3lp9q7] 2025, Nov 11. Support Vector Machine (SVM) Algorithm - GeeksforGeeks. Published: 2025-10-24 | Updated: 2025-11-11
[gb1ju5] 2025, Nov 11. What Is a Support Vector Machine? - MATLAB & Simulink - MathWorks. Published: 2025-10-22 | Updated: 2025-11-11
[1rfn6v] 2025, Nov 09. Support vector machine - Wikipedia. Published: 2002-07-27 | Updated: 2025-11-09
[10wu6s] 2025, Nov 10. Support Vector Machines: A Simple Explanation - KDnuggets. Published: 2016-07-07 | Updated: 2025-11-10
[4zeqh9] 2025, Nov 11. 1.4. Support Vector Machines - Scikit-learn. Updated: 2025-11-11