State Space Models
(2025-11-26T14:06.030Z)
Perplexity Query
(2025-11-26T14:06
.030Z)
Question:
Write a comprehensive one-page article about "State Space Models".
Model: sonar-pro
State Space Models (SSMs) are a mathematical framework for describing and predicting how dynamic systems evolve over time, particularly when not all aspects of the system can be directly observed.
[jvr5i6]
[f64tbg]
Their significance lies in the ability to infer hidden internal states that drive observable behavior, making them essential for analyzing complex, real-world processes in fields such as engineering, machine learning, and finance.
[jvr5i6]
[f64tbg]
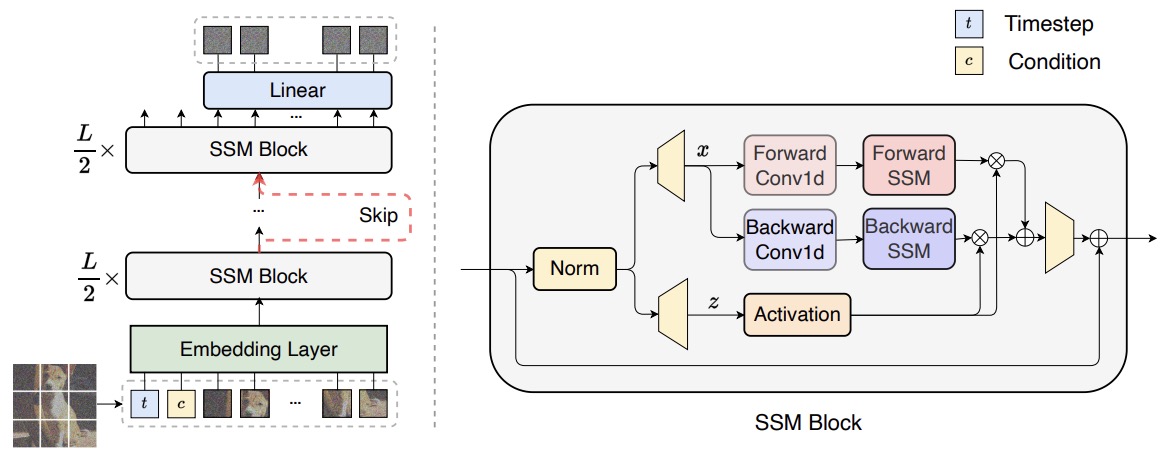
Understanding State Space Models
At their core, State Space Models consist of state equations and output equations that collectively describe how a system transitions from one state to another (the state equation) and how these internal states generate observable outputs (the output equation).
[f85gyh]
[f64tbg]
A state, often represented mathematically as a vector, encapsulates all the necessary information about the system at a specific time. The system’s evolution is governed by mathematical constructs—most commonly matrices labeled as A (state transition), B (input mapping), C (state-to-output mapping), and D (input-to-output mapping).
[jvr5i6]
For example, in a simple weather model, the hidden state might represent current atmospheric conditions, while the output could be temperature or rainfall measured at each timestep. Even though the true atmospheric variables can’t be seen directly, SSMs allow us to infer them and forecast future conditions by learning how the system’s state evolves.
[jvr5i6]
In practice, SSMs are powerful because they explicitly model uncertainty and noise. The hidden state is updated not just by deterministic rules but may also include random disturbances—crucial for handling messy real-world data. Unlike traditional time-series models (such as ARIMA), SSMs capture both sequential dependencies and structured system dynamics, making them ideal for modeling time-evolving systems with memory and hidden variables.
[f64tbg]
[035u87]
Examples and Applications
SSMs are used extensively in:
- Weather and climate forecasting: Modeling atmospheric dynamics to predict temperature or rainfall. [jvr5i6]
- Healthcare and medical monitoring: Tracking patient vitals or disease progression, where internal patient health is partially unobserved.
- Robotics and control systems: Guiding autonomous vehicles by estimating hidden positions and velocities. [f64tbg]

Benefits and Challenges
Key strengths of State Space Models include:
- Interpretability: Each component (A, B, C, D) has a clear, physical meaning, aiding model transparency and debugging. [f64tbg]
- Modularity: SSMs can be adapted to a wide range of linear and nonlinear systems, both deterministic and stochastic.
However, SSMs also present challenges:
- Computational Complexity: For very large-scale or highly nonlinear systems, computation may become demanding, though modern machine learning methods (such as neural SSMs) are rapidly improving efficiency. [f85gyh]
Current State and Trends
State Space Models are foundational in engineering and scientific fields, and their adoption is surging in data science, AI, and control systems.
[f64tbg]
[n2k6es]
Recent advances include the integration of SSMs with neural networks, enabling the modeling of highly nonlinear dynamics—so-called neural state-space models—which have become widely accessible through platforms like MATLAB and open-source machine learning frameworks.
[f85gyh]
[f64tbg]
Modern sequence modeling architectures, such as S4 and Mamba, leverage SSM principles to efficiently handle long-range dependencies, challenging recurrent neural networks (RNNs) and transformers for tasks like language modeling and time-series prediction.
[jvr5i6]
[f64tbg]
[qdgn2v]
Established technologies frequently combine SSMs with other machine learning strategies for improved scalability and interpretability, while leading organizations such as MathWorks, NVIDIA, Hugging Face, and academic labs remain at the forefront of development.
[f85gyh]
[f64tbg]
[qdgn2v]

Future Outlook
The future of State Space Models is poised for continued expansion, particularly as AI systems demand more interpretable, robust, and data-efficient approaches to sequence modeling. Advances in neural SSMs and scalable SSM algorithms may unlock new applications across autonomous machines, healthcare diagnostics, financial forecasting, and scientific discovery. As models become more accessible and integrated into mainstream AI pipelines, their impact is likely to grow, improving our ability to reason about and predict complex dynamic systems.
[jvr5i6]
[f64tbg]
Conclusion
State Space Models provide a powerful, interpretable, and versatile framework for understanding complex, dynamic systems. As technology evolves, SSMs are set to play an increasingly central role in AI, engineering, and data-driven sciences, helping us reveal the hidden structure of the world’s most challenging temporal phenomena.
Citations
[jvr5i6] 2025, Nov 26. What are State Space Models (SSMs) - GeeksforGeeks. Published: 2025-11-25 | Updated: 2025-11-26
[f85gyh] 2025, Oct 10. What Are Neural State-Space Models? - MATLAB & Simulink. Published: 2025-01-01 | Updated: 2025-10-10
[f64tbg] 2025, Nov 20. Understanding State Space Models in Machine Learning ... - GoCodeo. Published: 2025-06-24 | Updated: 2025-11-20
[035u87] 2025, Oct 29. State Space Models — Introduction to Scientific Machine Learning .... Updated: 2025-10-29
[5]: 2025, Nov 25. Understanding State Space Models (SSMs) like LSSL, H3 ... - Tinkerd. Published: 2024-07-08 | Updated: 2025-11-25
[n2k6es] 2025, Nov 21. State space model - Scholarpedia. Published: 2019-06-13 | Updated: 2025-11-21
[qdgn2v] 2025, Nov 15.
. Published: 2024-07-17 | Updated: 2025-11-15