Semantic HTML

(2025-08-17T13:33.158Z)
Perplexity Query
(2025-08-17T13:33
.158Z)
Question:
Write a comprehensive one-page article about "Semantic HTML".
Response from sonar-pro:
Semantic HTML: Making Web Pages Meaningful and Accessible
Introduction
Semantic HTML refers to the use of HTML tags that convey the meaning and structure of webpage content, rather than just its appearance.
[icv3t1]
[ljim2x]
It is significant because it enables browsers, assistive technologies, and search engines to better understand and interact with web content, bridging the gap between human and machine interpretation. As the backbone of the web, semantic HTML matters for accessibility, SEO, and maintainability—making websites more inclusive and discoverable.
[0m4jkf]
[5yeyk6]
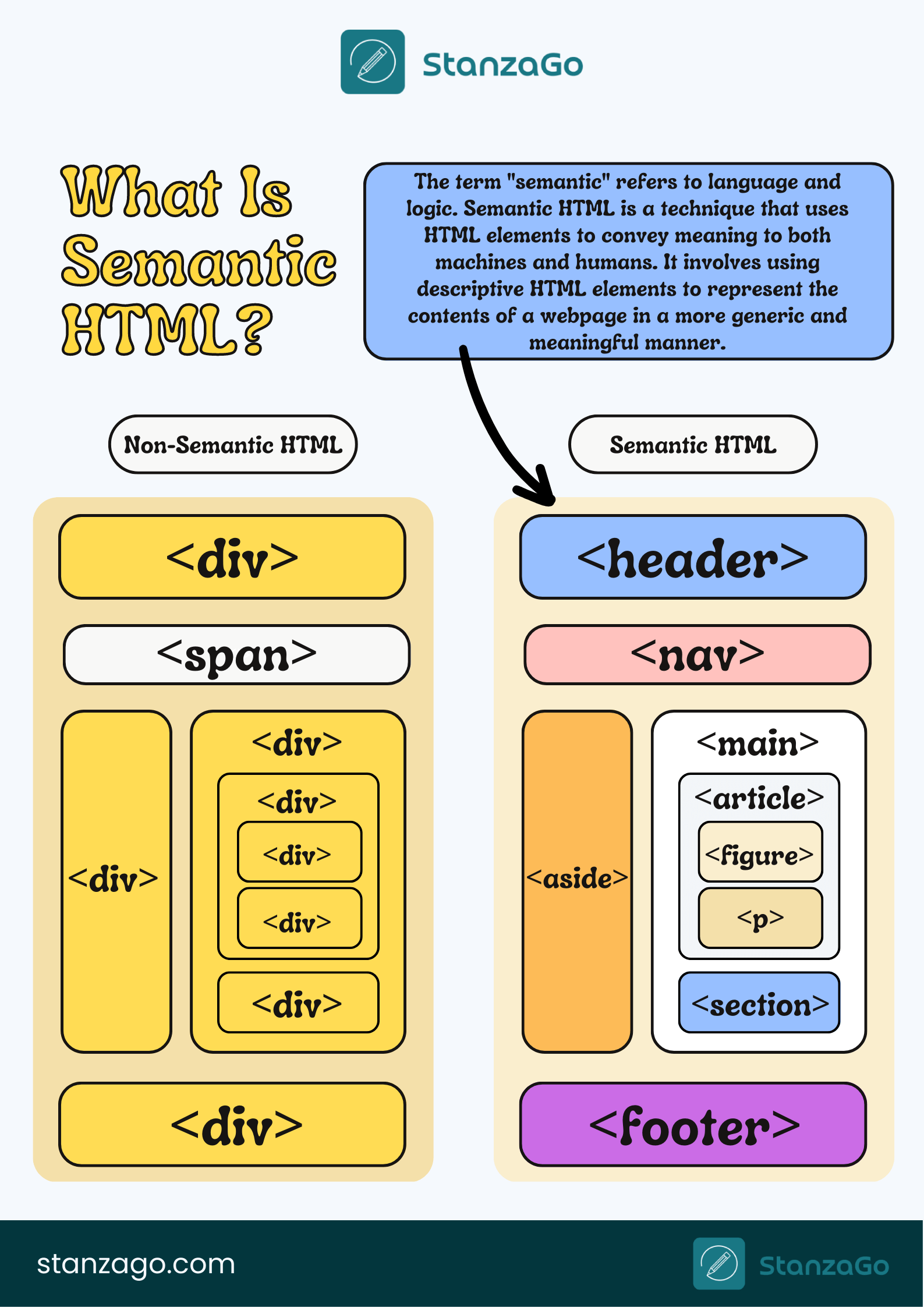
Main Content
Semantic HTML is built around elements that describe their purpose within the document, such as
**<header>**, **<nav>**, **<main>**, **<article>**, **<section>**, **<aside>**, and **<footer>**.
[730m65]
Using these elements properly helps organize content logically and gives deeper meaning to each part of a website. Instead of wrapping everything in generic <div> tags, semantic HTML allows developers to make clearer code structures, which are both easier to maintain and understand.
[5yeyk6]
For example, a basic blog post might use:
html
<article>
<header>
<h1>What is Semantic HTML?</h1>
<p>By Jane Doe</p>
</header>
<section>
<p>Semantic HTML improves accessibility and SEO...</p>
</section>
<footer>
<p>Posted on August 17, 2025</p>
</footer>
</article>This markup clearly separates the main content, header, and footer, making it easy for browsers and screen readers to interpret the page’s structure.
[730m65]
Common use cases include navigation menus (
<nav>), independent articles (<article>), and introductory headers (<header>), ensuring each section is used according to its semantic role.
[730m65]
The benefits of semantic HTML are substantial:
- User Experience: Clear organization helps all users comprehend and navigate content efficiently. [730m65]
Despite its advantages, challenges remain. Adopting semantic HTML requires developers to stay updated on best practices and new tags introduced in evolving standards. Misuse or overuse of certain elements can undermine their intent, while legacy systems may complicate transitions to more semantic structures. Training and awareness are necessary for consistent implementation, especially within larger development teams.

Current State and Trends
Semantic HTML has become a standard part of modern web development, especially since HTML5 introduced more comprehensive semantic elements. Most major frameworks—including React, Angular, and Vue—support semantic markup, though developers must apply best practices manually. Key technologies improving semantic HTML adoption include browser engines and assistive tools that rely on meaningful HTML structures for enhanced accessibility.
Recent developments center on legal requirements for digital accessibility, such as adherence to the Web Content Accessibility Guidelines (WCAG), making semantic HTML not just best practice but, increasingly, a compliance issue in many regions.
[icv3t1]
[0m4jkf]
The growth of voice and AI-powered assistants also bolsters demand for well-structured markup, as these platforms often rely on semantic cues to parse and deliver web content contextually.

Future Outlook
Looking ahead, semantic HTML will become more critical as digital accessibility and artificial intelligence continue to evolve. Future web standards may introduce new semantic tags or improve integration with device APIs. The expansion of immersive web technologies, such as voice-driven navigation and AI agents, is likely to heavily rely on meaningful HTML structures, pushing the web towards even greater machine readability and universal usability.
Conclusion
Semantic HTML transforms web pages into clear, accessible, and searchable documents—benefitting users, developers, and businesses alike. Its role will only grow as the web becomes more interactive and intelligent, shaping the future of digital communication.
Citations
[0m4jkf] 2025, Jul 13. What is Semantic HTML & Why Is It Important for Accessibility?. Published: 2023-05-18 | Updated: 2025-07-13
[icv3t1] 2025, Jun 16. What Is Semantic HTML? (And Why You Should Use It) - TheeDigital. Published: 2023-11-28 | Updated: 2025-06-16
[5yeyk6] 2025, Mar 04. Semantic HTML: Why it matters and top tips on how to apply it. Published: 2023-01-31 | Updated: 2025-03-04
[ljim2x] 2024, Dec 05. Semantic HTML tags - Locofy.ai. Published: 2024-05-21 | Updated: 2024-12-05
[730m65] 2024, Nov 20. Enhancing Accessibility with Semantic HTML. Published: 2024-02-12 | Updated: 2024-11-20