Primitive Data
(2025-08-17T04:59.511Z)
Perplexity Query
(2025-08-17T04:59
.511Z)
Question:
Write a comprehensive one-page article about "Primitive Data like Markdown, JSON, Markup".
Response from sonar-pro:
Primitive Data Types: Foundations of All Data
Primitive data types are the fundamental building blocks in computer programming, representing the most basic forms of data such as numbers, characters, and boolean values.
[nhnr26]
[mvjf05]
Their significance lies in enabling efficient data processing, optimized memory usage, and forming the base upon which all higher-level data constructs are built.
Understanding Primitive Data Types
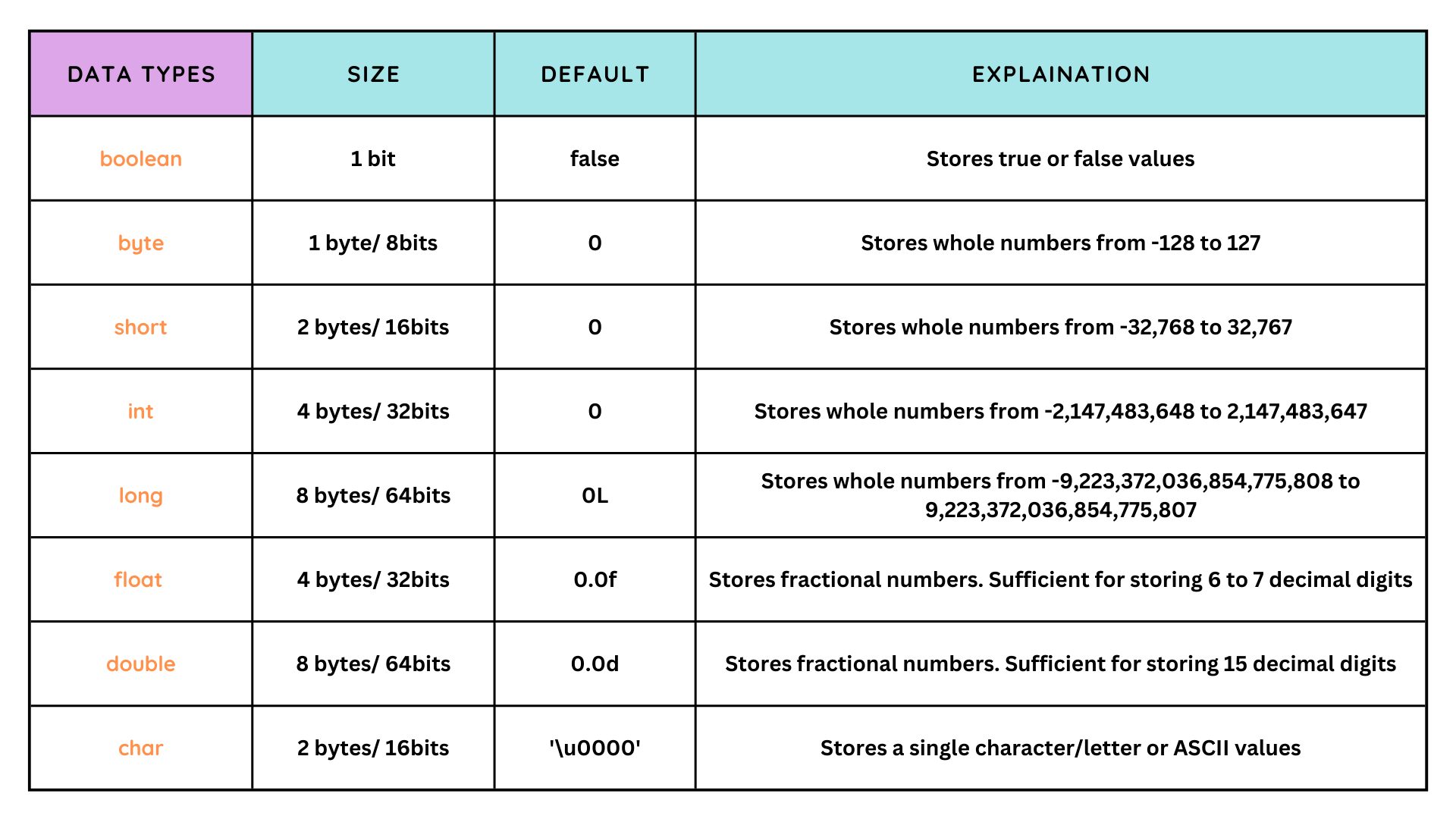
A primitive data type is defined as a basic, built-in data type offered by programming languages to represent simple and indivisible values—such as integers (
int), floating-point numbers (float, double), booleans (true/false), and characters (char).
[nhnr26]
[mvjf05]
These types are hardwired into the language or processor, granting direct access to system-level resources and predictable performance.For example, in Java, the key primitive data types are:
- int for integers
- float and double for floating-point numbers
- char for single characters
A core characteristic of primitives is their inability to be further broken down: an integer can't be subdivided within the type system into smaller data representations.
[nhnr26]
Unlike composite types (such as arrays or objects), primitives are standalone and directly encode data values.
Practical Examples and Use Cases
Primitive data types are ubiquitous across all software:
- Storing user age or count variables: To represent whole numbers, the
int(integer) type is ideal. [2cout6] - Boolean flags: Whether a feature is enabled or disabled is captured efficiently with a
booleanvalue. - Character storage:
charstores text input, such as initials or single keystrokes. - Floating-point values: Measurements, temperature, or calculations involving decimals use
floatordouble.
In code, assigning and manipulating primitives is direct. For example, swapping two
int values affects only those variables—their values are copied, ensuring isolation and performance.
[do6yak]
Benefits and Applications
- Low memory overhead: Unlike objects, primitives use minimal memory, which is crucial in systems programming or embedded environments.
- Foundation for abstraction: Structures, collections, and classes all build upon primitive types, making them indispensable to software development. [nhnr26]
Challenges and Considerations
- Limited expressiveness: Primitives cannot store complex relationships or behaviors.
- Fixed set: Each language offers a specific, unchangeable set of primitive types. [mvjf05] Customizing or extending primitives is not possible.
- Incompatibility with object paradigms: Primitives can't directly take advantage of object-oriented features without “boxing” or conversion into an object wrapper, sometimes reducing performance.
Current State and Trends
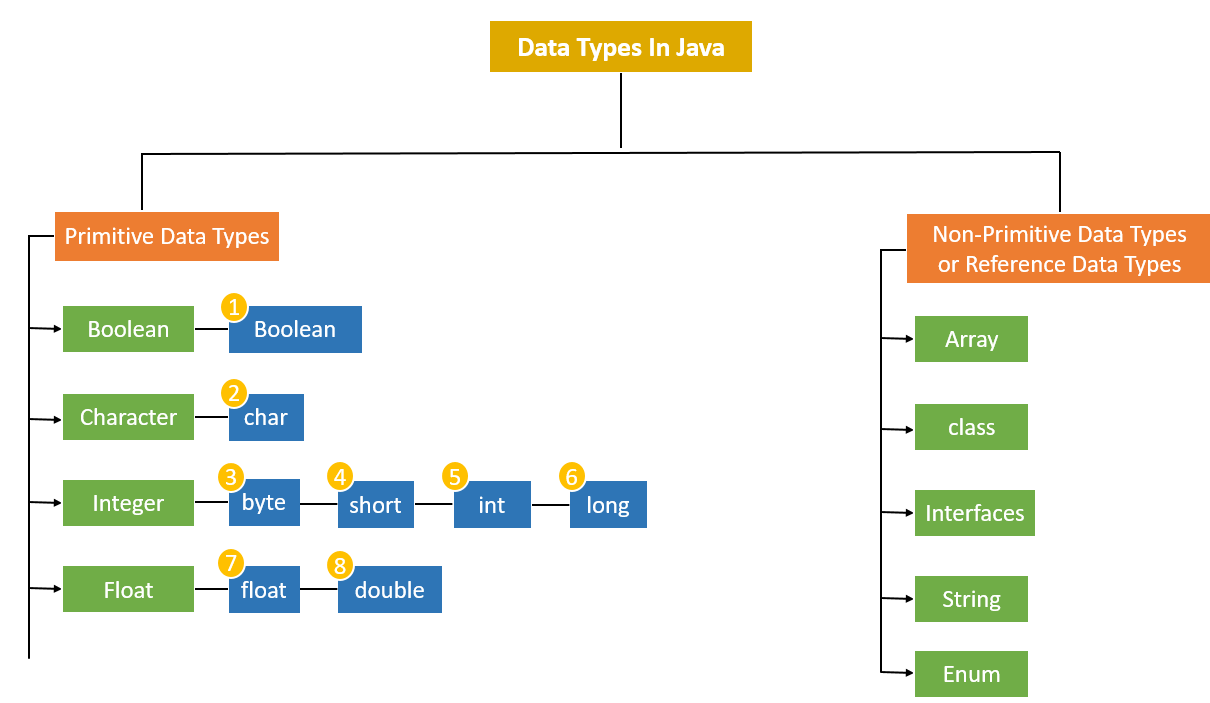
Primitive data types remain fundamental across programming languages, from C and Java to modern environments like Python and JavaScript.
[nhnr26]
[mvjf05]
The design and efficiency of primitives shape language performance and influence how programmers structure applications. The boundaries between primitives and objects are increasingly blurred: contemporary languages often offer “boxing” to permit primitives to be used interchangeably with objects, enabling uniformity in APIs (such as collections).
[do6yak]
Major technology platforms like Java, .NET, and Python continue to optimize how primitives are handled, supporting advances in virtual machines, compilers, and runtime performance.
Recent developments include the introduction of specialized primitives (e.g., new numeric types for cryptography) and hardware-level innovations that inform which primitives are exposed in system languages.
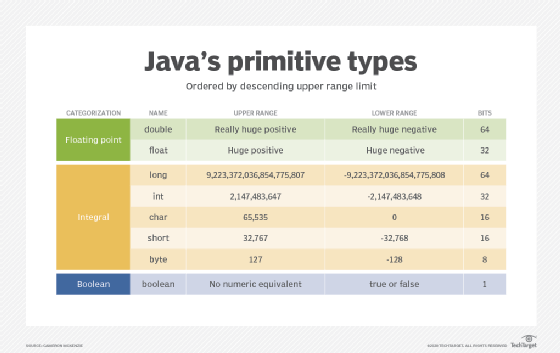
Future Outlook
As new application domains—like AI, IoT, and high-performance computing—push for even greater speed and efficiency, the design of primitive data types will remain a core area of innovation. Future trends may see the emergence of platform-specific primitives, seamless integration between primitives and complex types, and optimizations for cloud-based or parallel computing architectures.
Conclusion
Primitive data types are essential, providing the sturdy base upon which all digital information is processed and manipulated. As computing evolves, so too will the use and optimization of these foundational data elements, ensuring they remain relevant in an ever-shifting technological landscape.
Citations
[nhnr26] 2025, Jun 16. What are Primitive Data Types?: Complete Guide with Examples. Published: 2024-11-18 | Updated: 2025-06-16
[2cout6] 2025, Aug 03. Java Data Types - GeeksforGeeks. Published: 2025-07-23 | Updated: 2025-08-03
[mvjf05] 2025, Jul 14. Primitive data type - Wikipedia. Published: 2003-10-03 | Updated: 2025-07-14
[do6yak] 2025, Jul 24. Primitive data type vs. Object data type in Java with Examples. Published: 2025-07-12 | Updated: 2025-07-24
[85mk21] 2025, Jul 25. What do you understand by primitive data type? Give two examples.. Published: 2021-02-09 | Updated: 2025-07-25