Kanban
(2025-10-21T21:58.517Z)
Perplexity Query
(2025-10-21T21:58
.517Z)
Question:
Write a comprehensive one-page article about "Kanban".
Model: sonar-pro
Introduction to Kanban
Kanban is a visual Project Management methodology that helps teams and organizations improve workflow, increase efficiency, and deliver value continuously[2][3]. Originating from lean manufacturing in Japan, Kanban has become a cornerstone of Agile methodologies, especially in software development, IT operations, and knowledge work[1][5]. Its significance lies in its simplicity and adaptability—Kanban does not require radical changes to existing processes but rather seeks to optimize what is already there, making it a practical choice for organizations aiming for incremental improvement without disruption[1][3].

Main Content
Concept and MethodologyAt its core, Kanban visualizes work on a board (physical or digital), where tasks are represented as cards moving through different stages—typically “To Do,” “In Progress,” and “Done”[2][9]. This transparency allows teams to see the status of every task at a glance, identify bottlenecks, and manage workload limits to prevent overburdening (a practice known as “limiting work in progress”)[1][3]. Kanban is built on four key principles: start with what you do now, pursue incremental change, respect current roles and processes, and encourage leadership at all levels[1][3][4]. These principles emphasize working with existing workflows, making gradual improvements, and empowering every team member to contribute to process enhancement.
Practical Examples and Use CasesKanban is widely used in software development, IT support, marketing, and even manufacturing. For instance, a software team might use a digital Kanban board to track new feature development, with columns for “Backlog,” “Design,” “Development,” “Testing,” and “Deployment.” As tasks move from left to right, the team can quickly spot delays in testing and adjust resources accordingly. Similarly, a customer support team might visualize ticket resolution, ensuring that no agent is overwhelmed and that response times remain swift. The flexibility of Kanban allows it to be tailored to nearly any workflow, making it a versatile tool across industries[3][7].
Benefits and ApplicationsThe primary benefit of Kanban is improved visibility and flow, leading to faster delivery, reduced waste, and higher quality outcomes[7][9]. By limiting work in progress, teams avoid multitasking and context-switching, which can degrade productivity. Kanban’s focus on continuous, incremental change means organizations can adapt without the fear of disruptive overhauls—senior management sees quick wins, and teams experience less resistance to change[1][4]. Other applications include portfolio management, personal productivity, and even household task tracking, showcasing its broad utility[2].
Challenges and ConsiderationsWhile Kanban offers many advantages, it is not without challenges. Without proper discipline, boards can become cluttered, and work-in-progress limits may be ignored, negating the method’s benefits. Additionally, Kanban relies heavily on team collaboration and a culture of continuous improvement; if team members are resistant to transparency or change, the system may falter. Success with Kanban requires regular reviews, openness to feedback, and a willingness to experiment with small, data-driven changes[1][4].
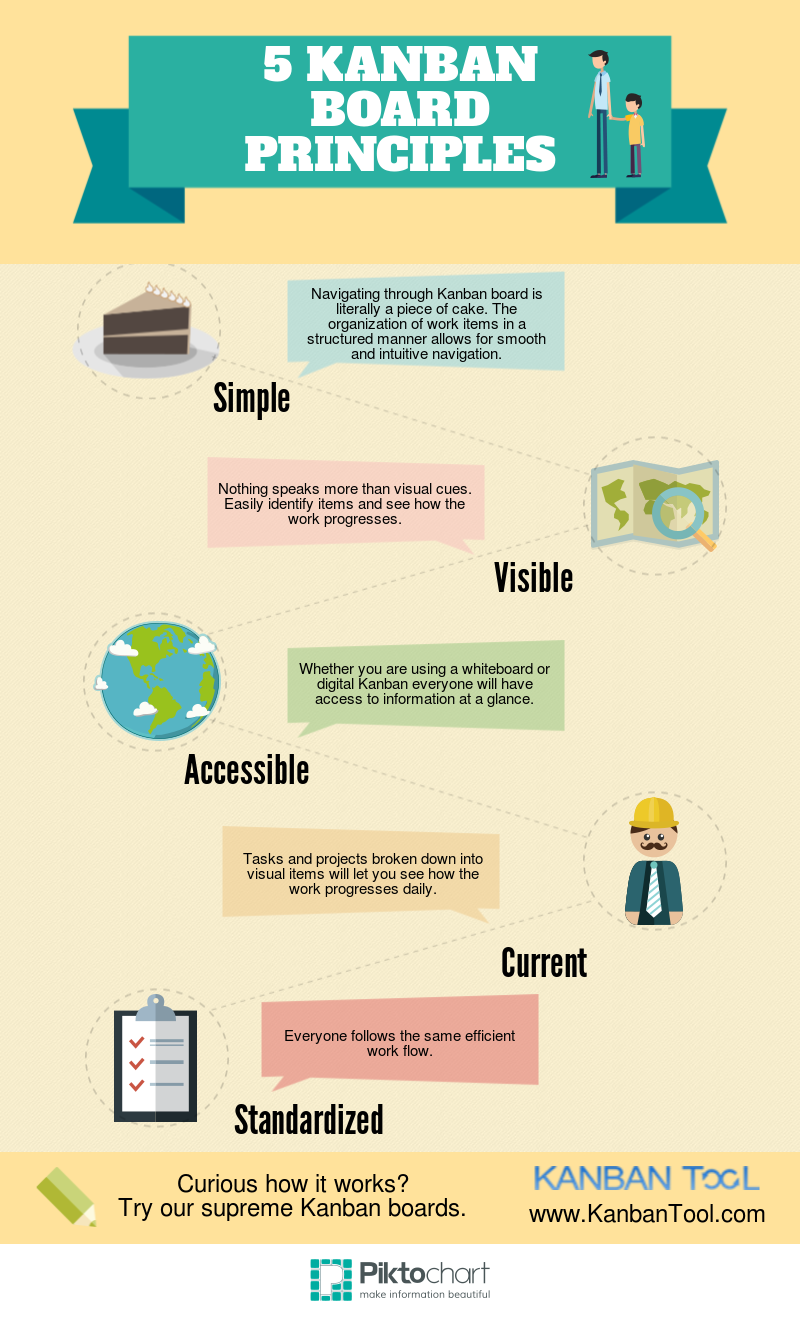
Current State and Trends
Kanban has seen widespread adoption, particularly in technology and service industries, as organizations seek more responsive and adaptable ways of working[5][7]. Digital tools like Jira, Trello, and Asana have made Kanban boards accessible to remote and hybrid teams, further driving adoption[8]. Leading consultancies and training organizations, such as Kanban University, offer certifications and guidance, emphasizing Kanban’s maturity as a professional discipline[5]. Recent trends include the integration of Kanban with DevOps practices, the use of analytics for predictive flow management, and the application of Kanban at scale across large, distributed organizations[5].
Key players in the space include not only software vendors but also thought leaders like David Anderson, who helped formalize the Kanban method for knowledge work[4]. The community continues to innovate, with new practices emerging around risk management, service delivery, and portfolio Kanban for executive oversight[5].
Future Outlook
Looking ahead, Kanban is likely to become even more deeply embedded in organizational culture as the demand for agility and continuous improvement grows. Advances in artificial intelligence and machine learning may lead to smarter Kanban systems that can predict bottlenecks and suggest optimal workflows. As remote and hybrid work models persist, digital Kanban tools will continue to evolve, offering richer integrations and more sophisticated analytics. Ultimately, Kanban’s principles of respect, empowerment, and incremental change position it as a sustainable approach for organizations navigating an increasingly complex and fast-paced world[5].

Conclusion
Kanban stands out as a practical, flexible, and empowering framework for managing work and driving continuous improvement. By focusing on visualization, flow, and incremental change, it delivers tangible benefits across a wide range of industries and use cases. As organizations face ever-greater demands for speed and adaptability, Kanban’s emphasis on respect, collaboration, and evolutionary progress ensures it will remain a vital tool for teams striving to achieve excellence in an uncertain future.
Citations
[1]: 2025, Oct 21. 4 Kanban Principles for Agile Project Management - Atlassian. Updated: 2025-10-21
[2]: 2025, Oct 17. What is Kanban - Principles and Implementation - GeeksforGeeks. Published: 2025-07-23 | Updated: 2025-10-17
[3]: 2025, Oct 21. The 4 core Kanban principles and 6 practices - Wrike. Published: 2025-09-25 | Updated: 2025-10-21
[4]: 2025, Oct 19. 4 Kanban Principles & 6 Practices for Better Workflows - Teamhood. Published: 2025-07-18 | Updated: 2025-10-19
[5]: 2025, Oct 21. The Official Guide to The Kanban Method. Published: 2021-03-01 | Updated: 2025-10-21
[6]: 2025, Oct 19. Kanban Principles and Practices Explained - Businessmap. Published: 2025-07-14 | Updated: 2025-10-19
[7]: 2025, Oct 21. Kanban Methodology: The Simplest Agile Framework - Kissflow. Published: 2025-09-16 | Updated: 2025-10-21
[8]: 2025, Oct 21. What Is Kanban? A Beginner's Guide for Agile Teams [2025] - Asana. Published: 2025-01-19 | Updated: 2025-10-21
[9]: 2024, Nov 10. What is Kanban? Learn About its Origins, Properties and Principles. Published: 2025-07-16 | Updated: 2024-11-10