Fine Tuning
(2025-07-23T09:54.236Z)
Perplexity Query
(2025-07-23T09:54
.236Z)
Question:
Write a comprehensive one-page article about "Fine Tuning".
Structure the article as follows:
- Introduction (2-3 sentences)
- Define the term and its significance
- Provide context for why it matters
- Main Content (3-4 paragraphs)
- Explain the concept in detail
- Include practical examples and use cases
- Discuss benefits and potential applications
- Address any challenges or considerations
- Current State and Trends (1-2 paragraphs)
- Discuss current adoption and market status
- Mention key players or technologies
- Highlight recent developments
- Future Outlook (1 paragraph)
- Predict future developments
- Discuss potential impact
- Conclusion (1-2 sentences)
- Summarize key points
- End with a forward-looking statement
Important Guidelines:
- Keep the total length to approximately one page (500-800 words)
- Use clear, accessible language
- Include specific examples and real-world applications
- Make it engaging and informative for a general audience
- Use markdown formatting for structure
Image References:
Include
Fine-Tuning: Unlocking the Power of Pretrained Models
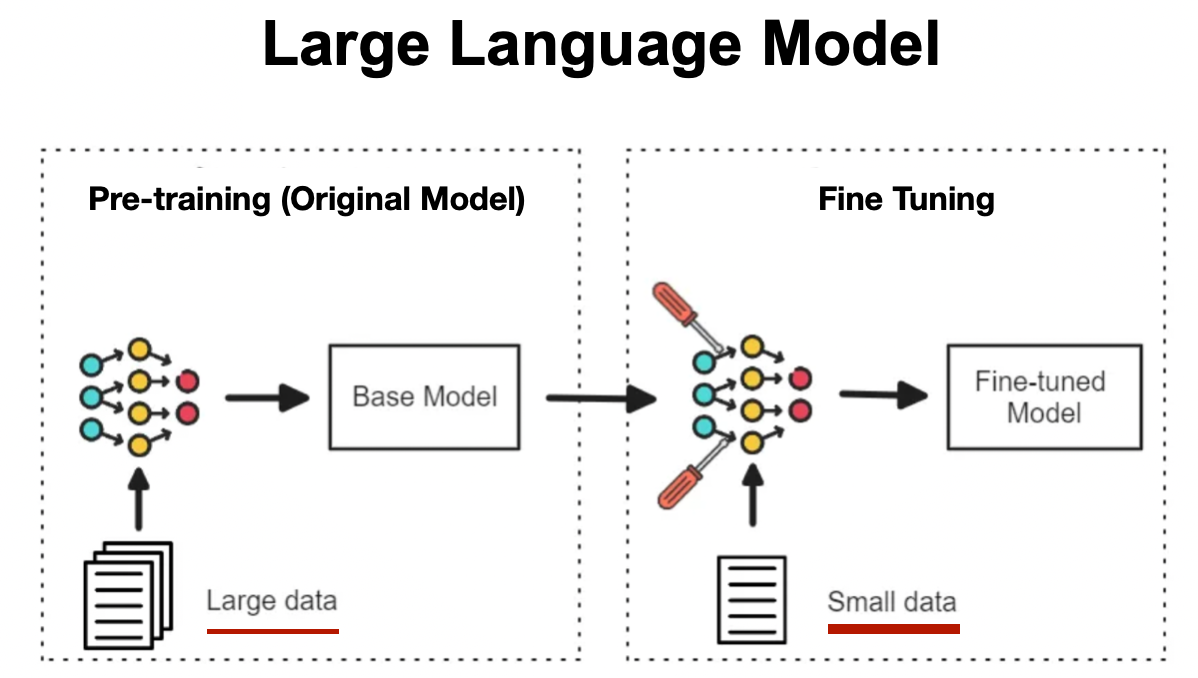
Fine-tuning is a pivotal concept in modern artificial intelligence (AI) and deep learning, referring to the process of taking a previously trained model and adapting it to perform a specific, often specialized, task. [^hm5ltz] [^slq980] This technique has revolutionized how AI solutions are developed, allowing organizations to build advanced, customized models using fewer resources and less data than ever before. [^slq980]
Understanding Fine-Tuning
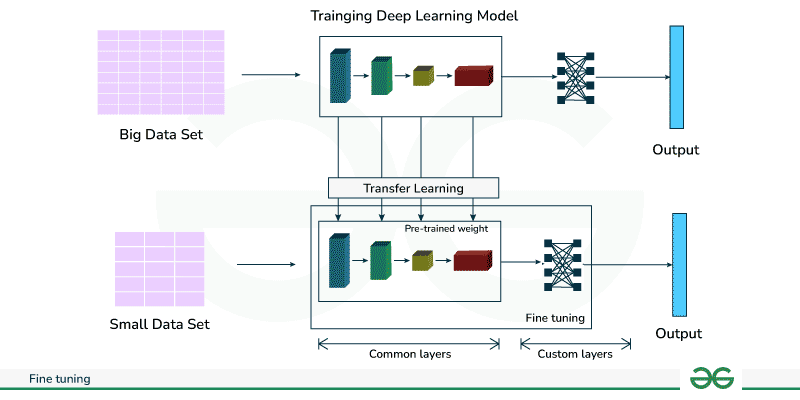
At its core, fine-tuning leverages the knowledge embedded in large, pretrained models—such as those used for language or image recognition—and refines that knowledge for new, narrower tasks. [^x9j9r8] [^slq980] Instead of training a model from scratch, which is time-consuming and costly, fine-tuning starts with a general-purpose model (for example, a language model like BERT or GPT) that has already learned from a vast and diverse dataset. [^4a4kmv] [^hm5ltz] Developers then expose the model to a smaller, domain-specific dataset, retraining select parts of the neural network so it can excel at the desired application (such as recognizing medical terminology or interpreting satellite images). [^4a4kmv] [^x9j9r8]
A typical fine-tuning process involves freezing the early layers of the model—which have learned basic patterns such as edges in images or general language structures—and only updating the later layers that specialize in task-specific features. [^4a4kmv] This selective approach means less data and computation are needed: basic knowledge is reused, while only necessary adaptations are made. [^hm5ltz] [^x9j9r8]
Practical Examples and Use Cases
Fine-tuning’s versatility is best illustrated through real-world applications:
- Customer Support Chatbots: By fine-tuning a large language model on company-specific documentation and chat logs, organizations create AI agents capable of answering customer queries with increased relevance and accuracy. [^hm5ltz]
- Medical Imaging: Pretrained computer vision models can be fine-tuned on annotated medical scans to detect diseases or abnormalities, even with limited additional data, greatly accelerating development in healthcare diagnostics. [^slq980]
- Sentiment Analysis: A sentiment analysis model can be fine-tuned for specific domains—such as finance or movie reviews—so it can better interpret the unique language and expressions of that context. [^x9j9r8]
These examples highlight how fine-tuning allows AI to be quickly and effectively adapted for industries with specialized vocabularies, data types, or operational requirements.
Benefits and Applications
The primary benefits of fine-tuning include:
- Efficiency: Models require less computational power and training time, as only specific parts are retrained. [^slq980]
- Data Savings: The need for large, labeled datasets is dramatically reduced since the model’s foundational knowledge is reused. [^hm5ltz]
- Customization: Models can be easily tailored for unique tasks or business needs without losing their general capabilities. [^hm5ltz]
As a result, fine-tuning is instrumental across a wide range of fields, from financial analysis and scientific research to creative industries and personalized digital assistants. [^x9j9r8] [^slq980]
Challenges and Considerations
Despite its advantages, fine-tuning is not without challenges. Training on too small or unrepresentative datasets can lead to overfitting, where the model becomes too specialized and loses versatility. [^4a4kmv] Ensuring data privacy and managing domain shifts—when new data differs significantly from the original training set—are also important considerations. [^x9j9r8] Careful selection of the underlying model and the right amount of retraining is key to successful fine-tuning.
Current State and Trends
Fine-tuning is now a cornerstone of modern AI development, especially with the rise of foundation models and large language models (LLMs). Major technology companies such as OpenAI, Google, Meta, and IBM offer platforms and APIs that facilitate easy, robust fine-tuning for both enterprise and individual developers. [^slq980]
Recent advancements include:
- The proliferation of open-source models and toolkits for fine-tuning, making the technique accessible to virtually any developer.
- Integration of automated fine-tuning workflows in cloud AI services, streamlining the adaptation process for business applications.
- Ongoing research into techniques such as parameter-efficient fine-tuning (PEFT), which further reduces computational requirements.
Future Outlook
Looking ahead, fine-tuning is poised to become even more efficient and impactful as new techniques emerge that require even fewer computational resources. As foundation models expand in capability, the reliance on fine-tuning will only increase—enabling more personalized, accessible, and secure AI systems across industries. Advances in federated learning and privacy-preserving fine-tuning will help broaden adoption, especially in healthcare and finance.
Conclusion
Fine-tuning empowers organizations to rapidly and efficiently adapt AI for specialized tasks, delivering tailored performance with minimal additional data and expense. As both technology and best practices evolve, fine-tuning will remain at the core of the AI revolution, driving innovation in how machines learn and serve humanity’s diverse needs.
Deprecation Warning
The ```yaml toolingGallery syntax is deprecated. Please use :::tooling-gallery directive syntax instead.
⚠️ Tool(s) not found:
tag: Fine-Tuners
(2025-07-23T10:00.858Z)
Perplexity Query
(2025-07-23T10:00
.858Z)
Question:
Please create a comprehensive list of technologies, frameworks, and web applications that are involved in the process of "Fine Tuning" an open source AI Model. Link to the websites of those services. Describe their differentiators, core competencies, and target user and customer base. Why use this over some other one?
Please reference technology media, as well as user generated content communities like reddit, hackernews, youtube, and hugging face
Model: sonar-pro
Response from sonar-pro:
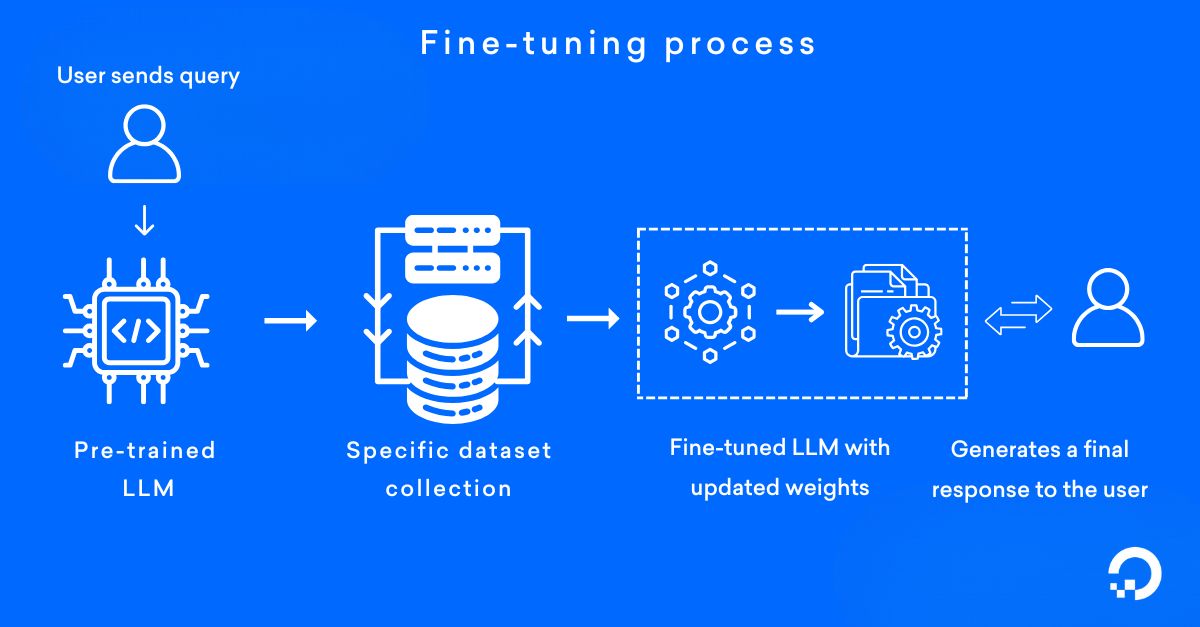
Fine-tuning an open-source AI model—typically a large language model (LLM)—involves a multi-layered stack of frameworks, toolkits, web applications, and infrastructure technologies. Below is a comprehensive, structured overview of the key tools and services used in this domain, with differentiators, target users, and short guidance on where each shines as reported by both technology media and community-driven content.
Core Technologies & Frameworks for Fine-Tuning LLMs
1. Hugging Face Transformers
- Website: huggingface.co/transformers
- Differentiators: Industry-standard library supporting an extensive collection of pre-trained and community models (e.g., LLaMA, Mistral, Mixtral, GPT-2/3).
- Core Competencies: Easy fine-tuning APIs; seamless integration with Hugging Face Hub datasets and models; large ecosystem and community support; strong documentation.
- Target Users: Researchers, developers, enterprises prototyping or customizing NLP models.
- Why use it: Most documented; broadest ecosystem; cutting-edge innovations appear first here. [^4cxmfm] [^d3afg9]
2. Axolotl
- Website: github.com/OpenAccess-AI-Collective/axolotl
- Differentiators: Streamlined pipeline for fine-tuning LLMs with modern features (e.g., QLoRA, LoRA adapters, multi-GPU, DeepSpeed).
- Core Competencies: Highly configurable YAML-driven workflows; support for parameter-efficient tuning; designed for scaling across GPUs.
- Target Users: Beginners (for ease-of-use) and advanced users (for distributed training).
- Why use it: Recommended for beginners and for anyone looking to scale training beyond a single GPU. [^yf67h5]
3. Unsloth
- Website: github.com/unslothai/unsloth
- Differentiators: Focuses on memory efficiency and reducing VRAM requirements when fine-tuning large models.
- Core Competencies: Patch existing Hugging Face models to significantly lower memory overhead; ideal for consumer-grade GPUs.
- Target Users: Hobbyists and professionals with limited GPU resources.
- Why use it: Essential when you need to fine-tune big models but lack server-scale hardware. [^yf67h5] [^4cxmfm]
4. Torchtune
- Website: github.com/pytorch/torchtune
- Differentiators: Pure PyTorch interface for fine-tuning LLMs; leans into customization and research-centric experimentation.
- Core Competencies: Leverages native PyTorch features; transparent and modifiable pipeline; ideal for research.
- Target Users: PyTorch developers, academic researchers.
- Why use it: Preferred if you want maximum flexibility and transparency using standard PyTorch tools. [^yf67h5]
5. DeepSpeed
- Website: microsoft.github.io/DeepSpeed
- Differentiators: Optimized for memory and compute efficiency; parallelism at multiple levels.
- Core Competencies: Used for massive-scale distributed training; supports ZeRO, LoRA, quantization.
- Target Users: Enterprise teams training massive models, researchers scaling past 1B-parameter models.
- Why use it: If training cost, memory, and speed are pivotal, especially on large infrastructure. [^4cxmfm]
6. LLaMA-Factory
- Website: github.com/hiyouga/LLaMA-Factory
- Differentiators: Comprehensive support for model fine-tuning, inference, and deployment with LLaMA-family models.
- Core Competencies: Simplifies process for the popular LLaMA/Mistral/Mixtral family; supports LoRA/QLoRA/other PEFT.
- Target Users: Practitioners working specifically with LLaMA derivatives.
- Why use it: Go-to when exclusively targeting Meta’s LLaMA ecosystem. [^4cxmfm]
7. Hugging Face Datasets
- Website: huggingface.co/docs/datasets
- Differentiators: One-stop shop for high-quality, community-curated datasets; integrates natively with Transformers.
- Core Competencies: Streamlines data prep, cleaning, and loading; efficient loading even for massive corpora.
- Target Users: Everyone from students to enterprise teams working with NLP/AI. [^d3afg9]
8. LiteLLM and VLLM
- Websites: github.com/BerriAI/litellm, github.com/vllm-project/vllm
- Differentiators: For inference and serving; not for fine-tuning itself, but essential for deploying/benchmarking custom models post-tuning.
- Core Competencies: LiteLLM offers OpenAI-style inference endpoints for custom/finetuned models; VLLM shines with throughput and efficient GPU utilization.
- Target Users: Teams and individuals deploying private LLM endpoints.
- Why use them: If you need robust, scalable endpoints for inference on fine-tuned models. [^4cxmfm]
Supporting Tools, Web Apps, and Ecosystem Services
- Weights & Biases (wandb.ai): Experiment tracking, hyperparameter sweeps, logging. [^4cxmfm]
- Comet ML (comet.ml): Advanced experiment management and collaboration.
- SkyPilot (skypilot.run): Cloud-native orchestration and cost-optimal multi-cloud training for LLMs. [^4cxmfm]
- OpenLLM (github.com/bentoml/OpenLLM): For production model deployment using open models.
- Google Colab and Kaggle Kernels: Entry-level cloud GPU environments, especially for hobbyists and learners.
Fine-Tuning Techniques & Advanced Methods
- LoRA/QLoRA (Low-Rank Adaptation): Efficient, storage-saving adapters for parameter-efficient fine-tuning—now standard in almost all frameworks above. [^vfst9z]
- PEFT (Parameter Efficient Fine-Tuning): Broader category including LoRA, adapters, and prefix tuning.
- RLHF (Reinforcement Learning from Human Feedback): Implemented with techniques like DPO or PPO for aligning model behavior with human preferences (most common at larger organizations and some advanced OSS projects). [^vfst9z]
Community and Discussion Platforms
- Reddit (r/LocalLLaMA, r/LocalGPT, r/HuggingFace): Extensive guides and troubleshooting; beginners and practitioners discuss frameworks and hardware adaption.
- HackerNews: Focus on “state of the art” announcements, case studies from emerging frameworks (e.g., migration from DeepSpeed to Unsloth for budget training).
- YouTube: Tutorials on fine-tuning pipelines, typically favoring Hugging Face and Axolotl (e.g., “Fine-tuning LLaMA 3 on your own data” videos).
- Hugging Face Forums: Q&A and advanced experimentation threads.
Why Choose One Over the Others? (Summary Table)
| Framework | Key Strength | Best For | Uniqueness |
| Transformers | Ecosystem & documentation | Rapid prototyping; general use | Most models supported |
| Axolotl | Beginner & multi-GPU scaling | First-time fine-tuners; scaling | YAML config, LoRA/QLoRA ready |
| Unsloth | VRAM/memory efficiency | Home labs, budget GPUs | Hugging Face patch, min. RAM |
| Torchtune | PyTorch native & customization | PyTorch power users, researchers | Transparent, hackable pipeline |
| DeepSpeed | Extreme scaling | Enterprise, academia, distributed setups | ZeRO/parallel/efficiency tricks |
| LLaMA-Factory | LLaMA model optimization | LLaMA/Mistral tuning and deployment | End-to-end LLaMA support |
Where to Start
- Beginners: Start with Hugging Face Transformers or Axolotl if you want configuration-driven, beginner-friendly flows, and strong community help. [^yf67h5] [^d3afg9] [^4cxmfm]
- Constrained hardware: Try Unsloth for VRAM-sensitive fine-tuning.
- Advanced custom research: Use Torchtune for maximum flexibility and transparency.
- Enterprise/distributed scale: DeepSpeed or SkyPilot.
- LLaMA exclusive: LLaMA-Factory.
Caveats:
- The ecosystem is rapidly evolving, and GPU/TPU availability or price often dictates the best tooling at a given time. [^4cxmfm] [^vfst9z]
- Some frameworks specialize: e.g., Unsloth for memory savings, DeepSpeed for massive parallelism; neither is a complete replacement for the other.
- Integration with experiment tracking (e.g., via Weights & Biases) is best practice for reproducibility and is natively supported in most modern frameworks.
For specifics, all tools and frameworks above have comprehensive docs and community links from their respective homepages.
Sources
[^4a4kmv] https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/deep-learning/what-is-fine-tuning/
[^hm5ltz] https://www.techtarget.com/searchenterpriseai/definition/fine-tuning
[^x9j9r8] https://telnyx.com/resources/what-is-fine-tuning-ai
[^slq980] https://www.ibm.com/think/topics/fine-tuning
[^j7q108] https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Fine-tuning_(deep_learning)
[^yf67h5] https://modal.com/blog/fine-tuning-llms
[^d3afg9] https://www.datacamp.com/tutorial/fine-tuning-large-language-models
[^vfst9z] https://arxiv.org/html/2408.13296v1
[^4cxmfm] https://substack.com/home/post/p-166090991
[^h4zoqk] https://community.openai.com/t/an-idea-for-an-open-source-framework-for-data-collection-and-llm-fine-tuning/389335