Desalination Technology
(2025-08-13T13:59.881Z)
Perplexity Query
(2025-08-13T13:59
.881Z)
Question:
Write a comprehensive one-page article about "Desalination Technology".
Response from sonar-pro:
Desalination Technology
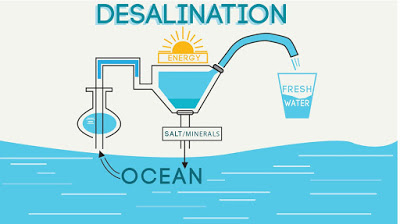
Desalination technology refers to the set of processes designed to remove salts and minerals from saline water, most commonly seawater, to produce fresh, potable water. As the global need for clean drinking water intensifies—especially in arid and densely populated regions—desalination has emerged as a critical solution to offset water scarcity and support sustainable development.
[pn9gxf]
[tjd579]
[y4n7gn]

Understanding Desalination: Processes and Principles
At its core, desalination separates fresh water from dissolved salts using either thermal or membrane-based techniques. The most widely employed methods today include:
- Reverse Osmosis (RO): This process forces seawater under high pressure through a semipermeable membrane, allowing water molecules to pass while rejecting salts and other impurities. RO is currently the leading technology due to its relatively high efficiency and modular scalability. [y4n7gn] [5d9dwe] [tjd579]
- Thermal Processes: Systems like multi-stage flash distillation (MSF) and multiple-effect distillation (MED) involve heating seawater so that it evaporates, leaving the salts behind. The vapor is then condensed to yield fresh water. Large installations, such as the MSF plant at Al-Jubayl, Saudi Arabia, produce hundreds of millions of liters daily through these methods. [tjd579] [pn9gxf]
A typical RO plant consists of pre-treatment (to safeguard membranes from fouling), high-pressure pumps, membrane modules, and post-treatment stages. Pre-treatment is especially crucial, ensuring suspended solids and potential contaminants are removed before water reaches the membranes.
[5d9dwe]
Practical Examples and Applications
Desalination is widely deployed in municipal and industrial contexts:
- The city of San Diego, California, operates one of North America’s largest desalination plants, supplementing local water supplies and enhancing drought resilience.
- Middle Eastern countries, including Saudi Arabia and the UAE, depend heavily on desalinated seawater to meet domestic and agricultural needs, with some producing over 750 million liters per day from single facilities. [tjd579]
- Islands and Small Coastal Communities, such as those in the Caribbean and Mediterranean, use small-scale or solar-powered desalination units to provide reliable water sources where fresh groundwater is scarce. [tjd579]
Desalination’s applications are not limited to drinking water; it supports industrial processes, irrigates crops, and even supplies water for energy generation.
Benefits include a virtually limitless water source (the ocean), independence from rainfall, and the potential for integration with renewable energy. However, challenges remain:
- High Energy Consumption: Current plants require significant power, often from carbon-intensive sources, raising ecological and cost concerns. [7eavtk]
- Brine Disposal: The concentrated salt byproduct ("brine") must be managed carefully to avoid harming marine ecosystems. [7eavtk]
- Infrastructure and Cost: High capital and operational expenses can be barriers, particularly in less developed regions. [tjd579]
Current State and Market Trends
Desalination is rapidly expanding, with over 20,000 plants operating globally, serving more than 300 million people.
[pn9gxf]
[tjd579]
Key players in the market include public utilities, multinational engineering firms, and regional consortiums in water-stressed areas.
- Technological leadership is evident in countries like Saudi Arabia, Israel, the United Arab Emirates, and Australia, each investing heavily in large-scale RO and thermal facilities.
- Research continues into advanced membranes, energy recovery devices, and zero-liquid discharge systems to improve efficiency and reduce environmental impacts.

Future Outlook
The future of desalination is poised for innovative breakthroughs, with rising investment in next-generation membranes, integration with renewable energy, and digital optimization for efficiency and sustainability. As climate change intensifies drought and depletes freshwater resources, desalination is expected to play an even more vital role in global water security, especially for coastal megacities and arid nations.
Desalination technology has transformed from a niche solution to a pillar of the modern water supply. As technological and ecological challenges are addressed, it will remain central to meeting the world’s growing water needs and fostering long-term resilience.
Citations
[y4n7gn] 2025, Jul 02. What Is Desalination? Definition, Pros and Cons. - Engineering. Published: 2021-09-28 | Updated: 2025-07-02
[7eavtk] 2025, Aug 04. The Process and Potential of Desalination - Last Energy. Updated: 2025-08-04
[pn9gxf] 2025, Aug 05. Desalination - Wikipedia. Published: 2002-12-11 | Updated: 2025-08-05
[tjd579] 2025, Aug 09. Desalination | Description, Process, & Production - Britannica. Published: 2025-08-08 | Updated: 2025-08-09
[5d9dwe] 2025, Aug 10. INTRODUCTION TO DESALINATION TECHNOLOGIES. Updated: 2025-08-10