Computer Architecture
Response from sonar-pro:
What is Computer Architecture?
 Computer architecture is the structural and functional design of a computer system's core components, including the processor, memory, and input/output controls, as seen from both hardware and software perspectives.
[nr9iur]
[f1ohsv]
This high-level blueprint determines how a machine executes instructions and interacts with programs, focusing on performance, reliability, and efficiency.
[nr9iur]
[f1ohsv]
Computer architecture is the structural and functional design of a computer system's core components, including the processor, memory, and input/output controls, as seen from both hardware and software perspectives.
[nr9iur]
[f1ohsv]
This high-level blueprint determines how a machine executes instructions and interacts with programs, focusing on performance, reliability, and efficiency.
[nr9iur]
[f1ohsv]

How Computer Architecture Differs from Chip Design:
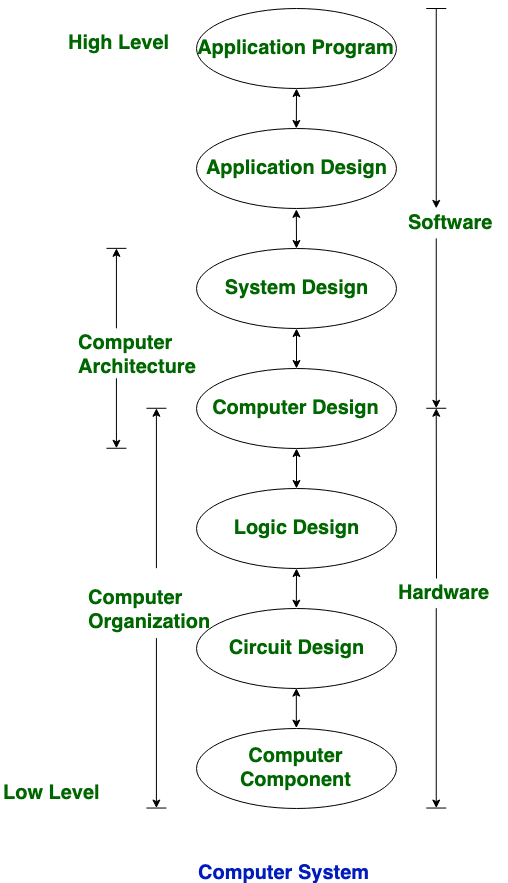
Major Inventors of State-of-the-Art Computer Architecture:
- John von Neumann: Defined the von Neumann architecture that underpins nearly all classical computers. [nr9iur]
- Seymour Cray: Invented several supercomputers, notably the CDC 6600 and Cray-1, introducing advanced pipelining and vector processing. [nr9iur]
- Jim Keller: Instrumental at AMD (K8, Zen), Apple (A4/A5 chips), and Tesla (AI chips) in CPU/microarchitecture design. [nr9iur]
- Yale Patt: Developed out-of-order execution and other performance improvements used in modern processors. [nr9iur]

Major Companies and Their Computer Architecture Revenue
| Company | Notable Architecture IP | Major Revenue Streams (2024) |
| ARM Holdings | ARM ISA and CPU cores | Licensing to Apple, Qualcomm, etc. |
| Intel | x86, Itanium, custom AI chips | CPUs (Data Center, PC), foundry services |
| AMD | x86 CPUs, Radeon GPUs, Zen core | CPUs, GPUs (Data Centers, Gaming, Licensed IP) |
| NVIDIA | GPU architecture (CUDA, AI, HPC) | GPUs, data centers, accelerated computing |
| Apple | ARM-based SoCs (A/M series) | Devices (iPhone, Mac), Vertical Integration |
| IBM | Power/POWER architecture | Enterprise servers, cloud, licensing |
 | ||
| [[Vocabulary/Field Programmable Gate Array | Field Programmable Gate Array]] Wikipedia Article |
- ARM Holdings (now public, owned by SoftBank): FY 2023 revenue ~$3.2 billion, primarily from IP licensing and royalties.
- Apple: Hardware devices (integrating proprietary ARM SoCs) drive >$200 billion in annual revenue, though their chip IP is not sold externally.
Computational Virtual Machines
 (A pie chart showing market share or revenue distribution among leading architecture/IP vendors.)
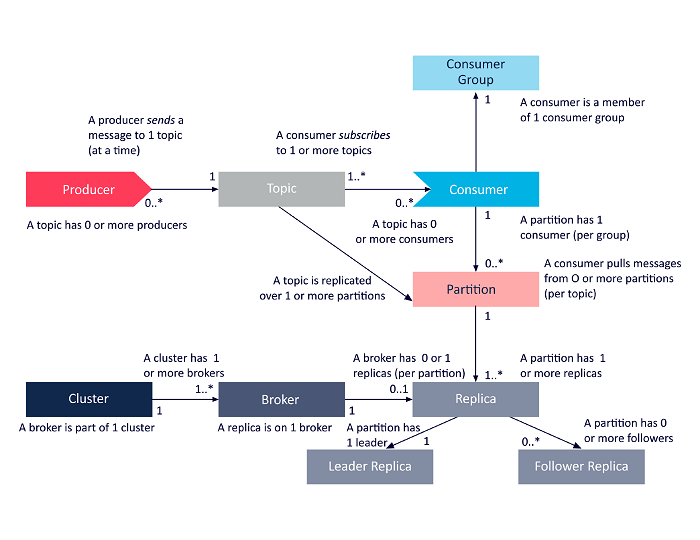
(A pie chart showing market share or revenue distribution among leading architecture/IP vendors.) Kafka architecture diagram showing producers, topics (with partitions), consumers, and brokers working together in a distributed system.
Kafka architecture diagram showing producers, topics (with partitions), consumers, and brokers working together in a distributed system.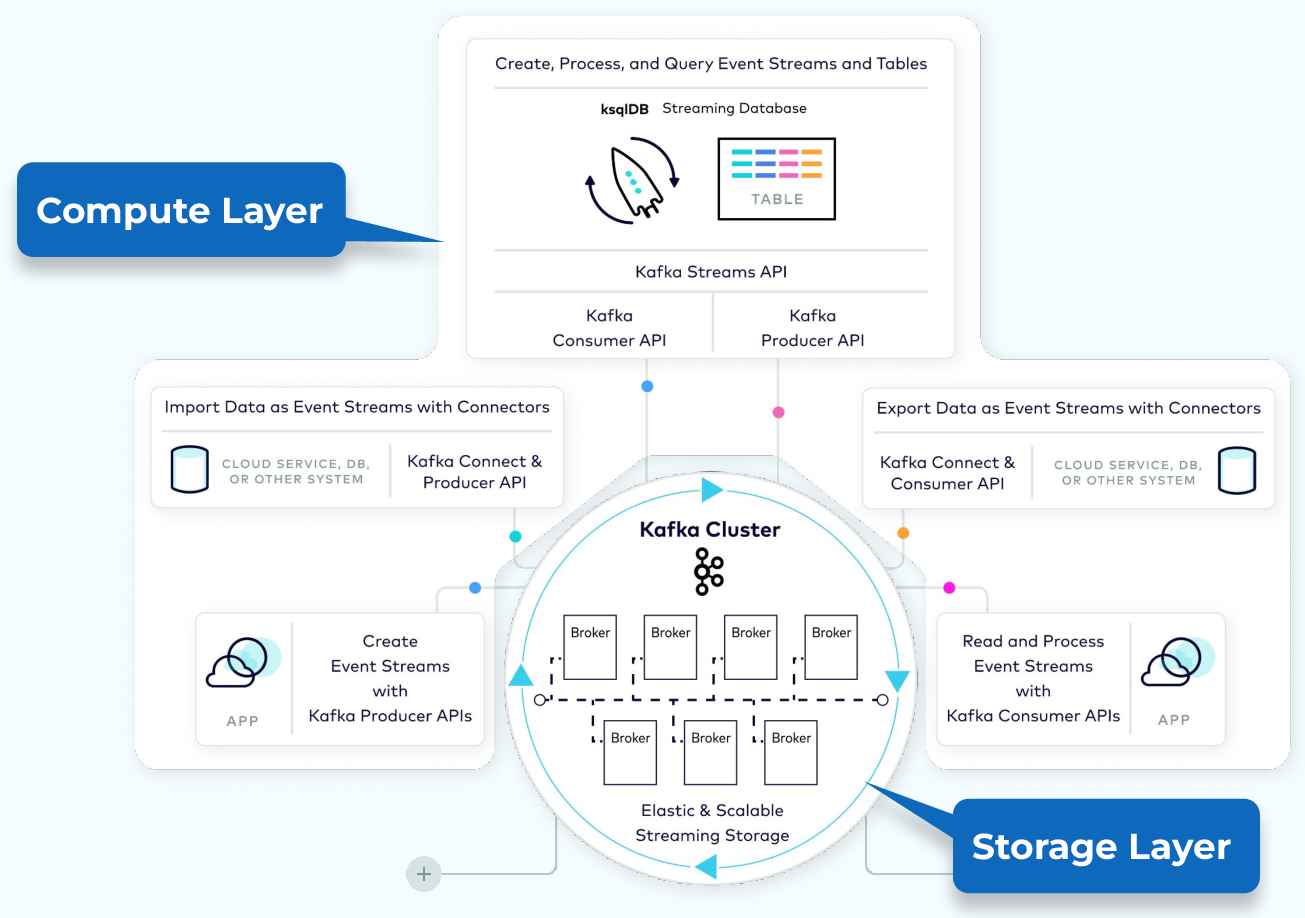
- What is it?
- What does it do?Kafka allows applications (called producers) to publish streams of records (messages) to named topics. Other applications (consumers) subscribe to topics and process the incoming data in real time. [n71xfk] [dlgxf7] [p0vxts]
- Four Core APIs:
- Producer API: Publish data to topics
- Consumer API: Subscribe to topics and consume data
- Streams API: Process streams of data in real time
Java: Programming Language and Software Platform
- What is it?Java is a general-purpose, object-oriented programming language and a software platform (the Java Virtual Machine, or JVM).
- What does it do?
- Programming Language: Java code is written by developers for building applications ranging from web servers, enterprise software, to Android apps.
- Platform (JVM): Java code is compiled into platform-independent bytecode, executed by the JVM. This provides portability—the same code runs on any device with a compatible JVM.
- Ecosystem: The Java ecosystem includes libraries, frameworks (like Spring), and tools that support many types of software, including distributed systems like Kafka.
Java is not itself a messaging or data streaming system—it is the foundation upon which applications (including Kafka) are often built.
Kafka vs. Java: Nature and Purpose
| Feature/Property | Kafka | Java |
| Category | Event streaming/messaging platform | Programming language and computational VM |
| Primary Function | Data ingestion, storage, and distribution | Writing and deploying software |
| Typical Use Case | Real-time analytics, log aggregation, event-driven services | General software: web, mobile, enterprise, IoT |
| How it works | Distributed cluster, producers/consumers, topics | Code compiled to bytecode, runs on JVM |
| Core APIs/Functions | Producer, Consumer, Streams, Connector APIs | Standard APIs, rich library and framework support |
| Relation | Often built using Java (Kafka is implemented in Java/Scala) | Can be used to build Kafka producers/consumers |

- Kafka is implemented in Java (and Scala), leveraging Java’s maturity and performance.
- Developers often use Java to write applications that send data to or consume data from Kafka clusters.
- Kafka: A real-time distributed platform for streaming and storing data, not a language. It enables high-throughput event-driven architectures.
- Java: A language and runtime for building all kinds of applications, including those that interact with or form part of Kafka-based systems.
Response from sonar-pro:
- Java: Runs on the Java Virtual Machine (JVM). The JVM is notable for supporting many additional languages beyond Java, such as Scala, Kotlin, Groovy, JRuby, Jython, Clojure, and more, by translating source code into JVM bytecode. [1nfskw] [od46nc] [7hn9qh] [IMAGE 1: Relevant diagram or illustration related to JVM and multi-language support]
- Python: Standard implementation (CPython) operates with a Python Virtual Machine (PVM), interpreting Python bytecode.
- ASP.NET Languages (C#, F#, VB.NET): Execute on the Common Language Runtime (CLR), the VM component of Microsoft's .NET framework. Languages compile to a common Intermediate Language (IL), which the CLR executes.
- JavaScript: Run on engines/VMs such as V8 (Google Chrome, Node.js), SpiderMonkey (Mozilla), and JavaScriptCore (WebKit).
- Smalltalk: Uses its own Smalltalk VM.
- Haskell: Has VMs such as the GHCi runtime for interpreted execution (but typically compiles to native code for production).
| Language | Virtual Machine | Notable Features |
| Java | JVM | Portability, multi-language, robust ecosystem |
| .NET langs | CLR | Multi-language, Windows integration |
| Python | PVM | Simplicity, extensive libraries |
| Ruby | YARV/JRuby | Dynamism, both native and JVM support |
| Erlang | BEAM | High concurrency, fault tolerance |
| JS | V8, JSC, SpiderMonkey | Just-in-time compilation, browser/server use |
| PHP | Zend Engine | Web scripting focus |
| Smalltalk | Smalltalk VM | Object-oriented, live environment |
| Lua | Lua VM | Lightweight, embeddable |
| Prolog | WAM | Suited for logic programming |
Links to Companies and Notable Inventors' Bios:
Notable Inventors:
Citations
[nr9iur] 2025, Jul 27. Computer architecture - Wikipedia. Published: 2001-10-16 | Updated: 2025-07-27
[62p53b] 2025, Aug 07. System on a chip - Wikipedia. Published: 2002-10-07 | Updated: 2025-08-07
[f1ohsv] 2024, Dec 19. Computer Architecture and Systems - NC State ECE. Published: 2023-05-16 | Updated: 2024-12-19
[yblc0d] 2025, Jul 31. "From Chip Design to Chip Learning" by Yunji CHEN, Zidong DU et al.. Updated: 2025-07-31
[g3b7mw] 2025, Jul 21. What is the difference between chip architecture, design and design .... Updated: 2025-07-21
[n71xfk] 2025, Aug 01. Apache Kafka® architecture: A complete guide, 2025. Published: 2025-06-03 | Updated: 2025-08-01
[q6cbsa] 2025, Jun 16. Apache Kafka Architecture: What You Need to Know | Upsolver. Published: 2022-07-29 | Updated: 2025-06-16
[p0vxts] 2025, Jun 16. Apache Kafka Architecture Deep Dive - Confluent Developer. Updated: 2025-06-16
[dlgxf7] 2025, Jul 22. What is Apache Kafka? Definition of Event Streaming Platform - AWS. Published: 2025-07-18 | Updated: 2025-07-22
[1nfskw] 2025, Jun 03. List of JVM languages - Wikipedia. Published: 2008-01-20 | Updated: 2025-06-03
[od46nc] 2025, Jun 16. A Complete Guide to JVM Languages - Whizlabs Blog. Published: 2021-03-04 | Updated: 2025-06-16
[no9zeq] 2025, Jun 16. List of Java virtual machines - Wikipedia. Published: 2006-04-08 | Updated: 2025-06-16
[7hn9qh] 2025, Aug 06. 14 JVM Languages for Software Development - spec india. Published: 2022-07-08 | Updated: 2025-08-06
[xwak0f] 2025, Apr 04. What other famous virtual/abstract machines are there other than the .... Published: 2021-03-21 | Updated: 2025-04-04