Blockchain
(2025-09-24T12:55.561Z)
Perplexity Query
(2025-09-24T12:55
.561Z)
Question:
Write a comprehensive one-page article about "Blockchain".
Model: sonar-pro
Transforming Digital Trust and Efficiency
Blockchain is a form of distributed ledger technology (DLT) that enables data to be securely recorded, shared, and managed across a network of computers without relying on a central authority.
[1uq6a6]
[dd1y5t]
[3iwv65]
Its significance lies in offering a transparent, tamper-proof system for tracking transactions, fostering trust, and streamlining processes in digital ecosystems. As digital interactions expand, blockchain’s unique approach to data integrity is increasingly vital for finance, supply chains, and beyond.
[dy2qxf]
[1uq6a6]

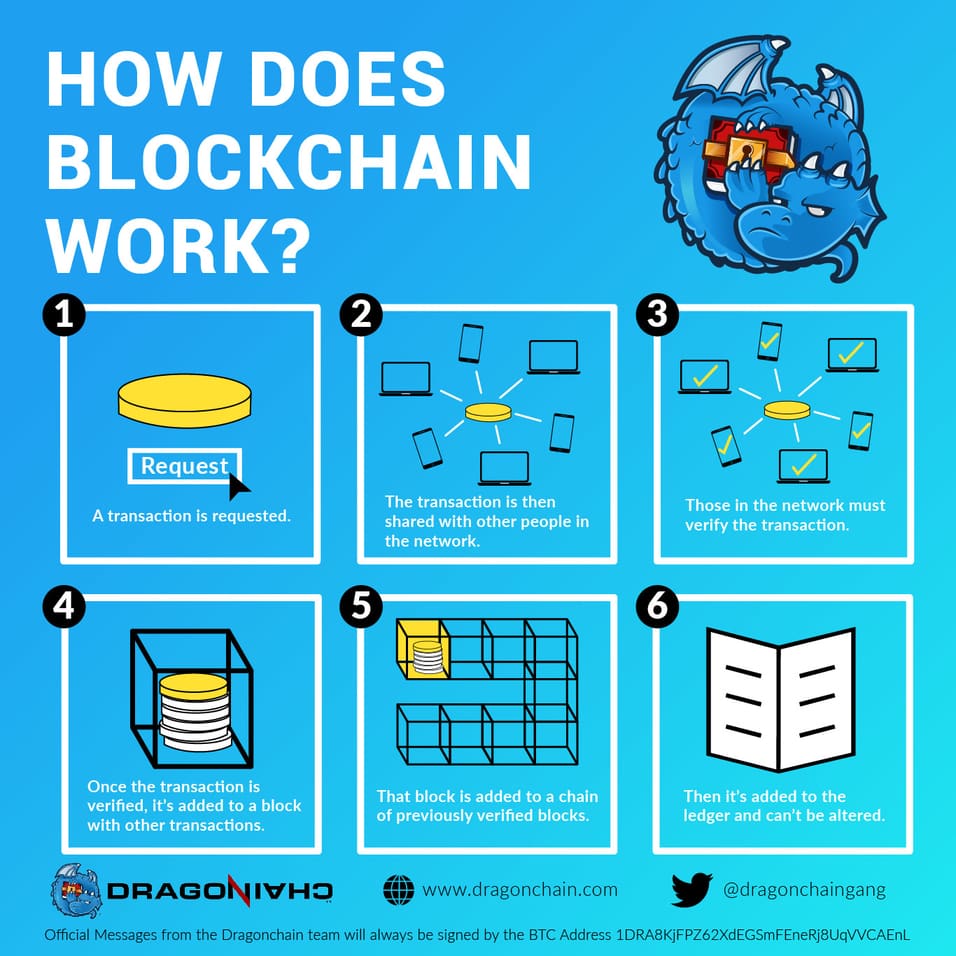
What Is Blockchain and How Does It Work?
At its core, blockchain is a decentralized database—a digital ledger—that keeps chronological records of transactions, referred to as blocks, linked together in an unbreakable chain.
[e8m4j0]
[3iwv65]
Each block contains transaction data, a cryptographic hash of the previous block, and a timestamp. Because copies of the blockchain are maintained and synchronized across a peer-to-peer network, altering any information requires consensus from the network, making fraudulent tampering nearly impossible.
[dy2qxf]
[dd1y5t]
Transaction verification relies on advanced cryptographic mechanisms and, in many blockchain systems, game theory to incentivize honesty.
[dy2qxf]
The first major blockchain use was Bitcoin, launched in 2009, which demonstrated how value could be exchanged securely and directly between users, bypassing traditional intermediaries such as banks.
[1uq6a6]
[3iwv65]
Unlike conventional databases, which store data in tables centrally, blockchains store data as a series of blocks distributed throughout the network.
[1uq6a6]
Practical Examples and Use Cases
Blockchain's best-known application is in cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin and Ethereum, where it enables decentralized, transparent, and secure peer-to-peer transactions.
[1uq6a6]
[dd1y5t]
However, blockchain is rapidly being adapted for diverse sectors:
- Supply Chain Management: Companies use blockchain to track products from origin to delivery, increasing transparency and reducing fraud. For example, IBM’s Food Trust system helps verify the authenticity and journey of produce.
- Healthcare: Patient records and consent forms are managed securely, with auditable histories, minimizing risks of data breaches.
- Digital Identity: Individuals control their own verifiable credentials, reducing identity theft and streamlining access to services.
- Smart Contracts: On blockchains like Ethereum, programmable contracts automatically execute transactions when predefined conditions are met, enabling innovation in areas such as insurance, real estate, and logistics. [dd1y5t]
Benefits and Challenges
Key benefits of blockchain include transparency, security, and immutability—once information is stored, it cannot be changed without wide consensus.
[dd1y5t]
[3iwv65]
Decentralization minimizes single points of failure and empowers users by removing powerful intermediaries, which can reduce costs and improve efficiency.
[1uq6a6]
[e8m4j0]
However, blockchain faces notable challenges:
- Scalability: Popular blockchains struggle to process high volumes of transactions quickly, creating bottlenecks.
- Energy Consumption: Consensus mechanisms like proof-of-work (used by Bitcoin) require significant computational resources.
- Regulatory Uncertainty: Legal frameworks around blockchain, especially cryptocurrencies, are evolving and vary by jurisdiction.
Current State and Trends
Blockchain adoption has accelerated across industries. Many financial institutions, technology firms, and governments are exploring or deploying blockchain-based solutions for payments, cross-border remittance, supply-chain integrity, and more.
[dd1y5t]
Companies like IBM, Microsoft, and Amazon Web Services offer blockchain-as-a-service platforms, while cryptocurrencies—including Bitcoin and Ethereum—remain central players in public blockchain networks.
[1uq6a6]
[dd1y5t]
Recent developments include the launch of scalable, energy-efficient blockchains using proof-of-stake consensus (seen with Ethereum’s upgrade) and the rise of decentralized finance (DeFi), which allows users to lend, borrow, and trade assets without intermediaries. Enterprises are piloting blockchain for regulatory compliance, digital voting, and secure information sharing.
[dd1y5t]

Future Outlook
As blockchain matures, integration with emerging technologies—such as artificial intelligence and the Internet of Things—could revolutionize automation, cybersecurity, and data management. Experts forecast wider mainstream acceptance, more efficient consensus protocols, and broader regulatory clarity, potentially redefining trust and collaboration in digital societies.
[dd1y5t]
In summary, blockchain is reshaping trust and efficiency in digital transactions, with far-reaching implications for business, technology, and society. As adoption grows, its transformative potential will likely expand well beyond its cryptocurrency origins.
Citations
[dy2qxf] 2025, Sep 24. Blockchain, explained | MIT Sloan. Published: 2017-05-25 | Updated: 2025-09-24
[1uq6a6] 2025, Sep 24. What is Blockchain? Definition, Examples and How it Works. Published: 2025-01-30 | Updated: 2025-09-24
[e8m4j0] 2025, Sep 24. What Is Blockchain and How Does It Work? - Black Duck. Published: 2025-07-10 | Updated: 2025-09-24
[dd1y5t] 2025, Aug 29. What is Blockchain Technology: Process, Types, Applications. Published: 2025-06-29 | Updated: 2025-08-29
[3iwv65] 2025, Sep 22. Blockchain - Wikipedia. Published: 2014-10-09 | Updated: 2025-09-22
[6]: 2025, Sep 24. What is Blockchain Technology? - AWS. Published: 2025-09-02 | Updated: 2025-09-24
[7]: 2025, Sep 24. What is blockchain technology? - McKinsey. Published: 2024-06-06 | Updated: 2025-09-24
[8]: 2025, Sep 24. Making sense of bitcoin, cryptocurrency and blockchain - PwC. Published: 2024-04-11 | Updated: 2025-09-24