AI Factories
Core Differences: AI Factories vs. Traditional Data Centers
| Aspect | Traditional Data Centers | AI Factory (AI Data Center) |
| Primary Purpose | General business apps (email, web, databases) | Large-scale AI model training, inference, and lifecycle |
| Hardware Focus | CPU-centric, limited GPUs | Accelerator-centric: massive GPU/TPU clusters, fast interconnects |
| Workloads | Mixed, unpredictable, often idle | AI/ML workloads: continuous, saturate hardware |
| Networking | Standard bandwidth, typical redundancy | Ultra-high speed (e.g., InfiniBand, RDMA), low-latency interconnects |
| Storage | Traditional storage, lower throughput | High-throughput tiers, often NVMe, for massive datasets |
| Cooling/Power | Standardized for moderate densities | Extreme density, advanced cooling (liquid, immersion), vastly higher power draw |
| Software Stack | OS, hypervisors, routine business software | ML frameworks (PyTorch, TensorFlow, Triton), model serving APIs, orchestration for AI |
| Lifecycle Focus | Static processing, limited automation | Fully integrated AI pipeline: data ingestion, model training, deployment, monitoring, retraining [2hscwa] [zheha3] [4qejn6] [2gzj18] [cy9bi7] |

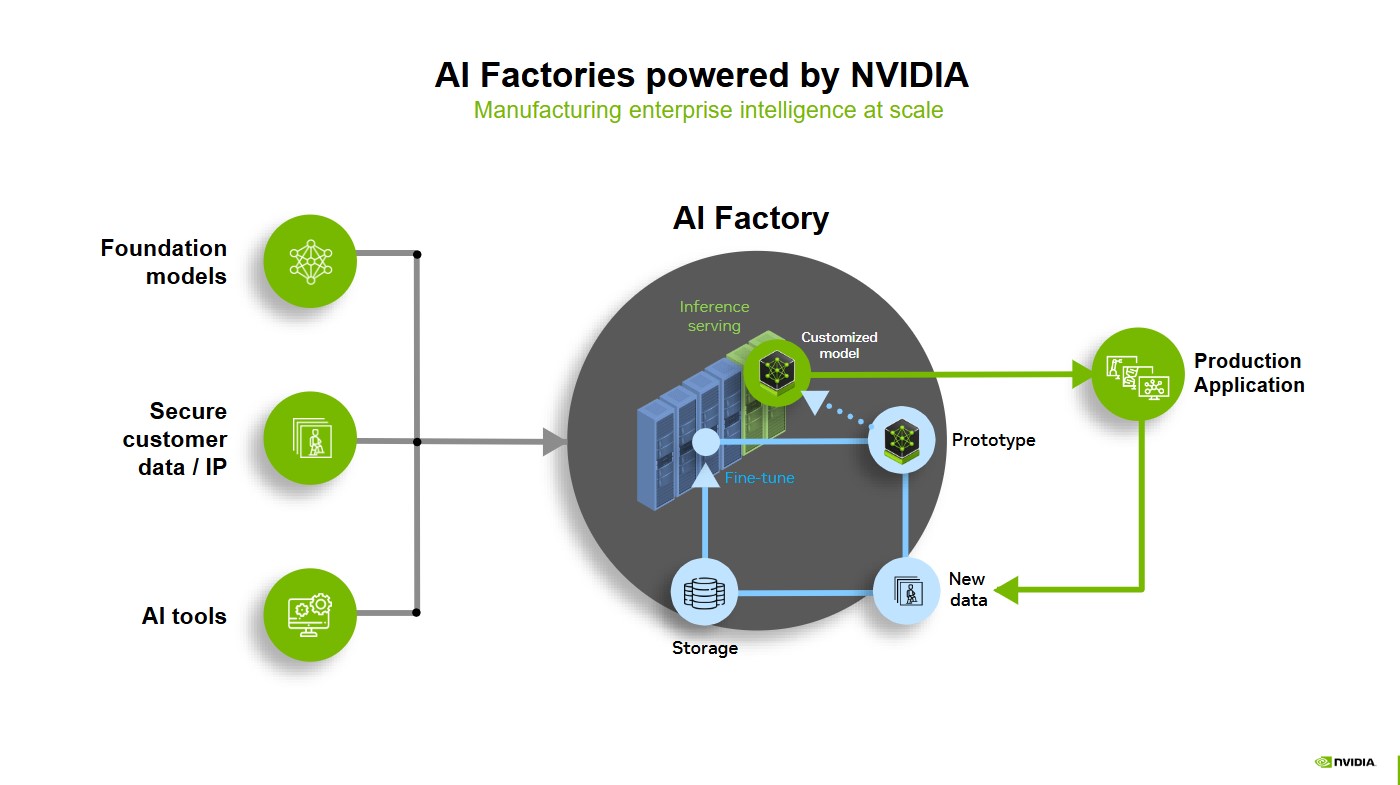
How AI Factories Work
- Accelerator hardware: Massive GPU clusters (e.g., NVIDIA H100), Tensor Processing Units (Google), sometimes custom AI chips.
- High-bandwidth connectivity: Technologies like NVLink, InfiniBand, and Remote Direct Memory Access (RDMA) enable GPUs and storage to communicate at ultrafast speeds, even across multiple servers.
- High-throughput storage: NVMe SSDs and distributed filesystems for rapid access to gigantic training datasets.
- Advanced scheduling/orchestration: Kubernetes, Slurm, or similar, with extensions for AI job placement, model versioning, and automatic scaling.
Technologies, Vendors, and Services
- Storage: Pure Storage, NetApp, DDN, custom NVMe fabrics.
- Networking: NVIDIA/Mellanox (InfiniBand), Arista (low-latency switches), Cisco (AI data center fabric).
- Hardware: NVIDIA (GPUs, networking), AMD (GPUs), Google (TPUs), Dell/HP (integrated AI servers), Supermicro (AI-optimized racks), IBM.
- Cloud Providers: Amazon Web Services, Google Cloud (with TPUs), Microsoft Azure (AI supercomputing clusters), Oracle Cloud.
- Managed AI infrastructure (hardware, networking, and orchestration provided as a service)
- AI model training platforms (Platform-as-a-Service for large-scale model runs)
- Data storage and data lake services
- Model serving and inference APIs

Unique Requirements and Advantages
- Scale: Designed for hundreds or thousands of tightly-coupled GPUs.
- Flexibility: Hybrid architectures, spanning on-premises, cloud, and edge deployments, unified by centralized management tools.
- Data and Model Sovereignty: Enhanced security and control for business-critical, proprietary data and models.
Citations
[2hscwa] 2025, Nov 22. AI Factories: What Are They and Who Needs Them? - Mirantis. Published: 2025-08-29 | Updated: 2025-11-22
[zheha3] 2025, Nov 21. What is an AI Factory? | NVIDIA Glossary. Published: 2025-06-11 | Updated: 2025-11-21
[516d89] 2025, Nov 23. What Is an AI Data Center? - IBM. Published: 2025-02-21 | Updated: 2025-11-23
[4qejn6] 2025, Nov 22. AI Factories: Separating Hype From Reality - Data Center Knowledge. Published: 2025-02-26 | Updated: 2025-11-22
[r5bqqf] 2025, Nov 23. What is an AI data centre, and how does it work?. Published: 2024-07-15 | Updated: 2025-11-23
[2gzj18] 2025, Nov 21. Understanding Artificial Intelligence Factories | AI Data Centre .... Published: 2024-03-12 | Updated: 2025-11-21
[j9nppw] 2025, Nov 23. What Is an AI Factory? - Trend Micro. Published: 2025-06-18 | Updated: 2025-11-23
[oa01ev] 2025, Nov 22. AI Factories Are Redefining Data Centers, Enabling Next Era of AI. Published: 2025-03-18 | Updated: 2025-11-22
[cy9bi7] 2025, Nov 22. From Data Centers to AI Factories: The Next Infrastructure Revolution. Published: 2025-10-15 | Updated: 2025-11-22